Contents

Explore how artificial intelligence (AI) will transform the delivery of patient care – an important function of the healthcare system.
AI is no longer an unfamiliar term to healthcare providers and patients. There are now various ways to employ AI, and the future emergence of new use cases is certain. Besides helping with administrative tasks and research, it is noteworthy how AI has been offering innovative approaches to patient care that benefit both the patients and medical workers.
The industry has already adopted AI and will continue to do so
The healthcare industry is under mounting pressure. According to the World Health Organization, by 2030, the sector may have a shortage of 9.9 million physicians, nurses, and midwives. However, hiring and training new employees is not enough.
There’s also a need to simplify their usually mundane, time-consuming tasks and make sure they have enough time caring for patients. Here’s how AI can help: it identifies patterns and obtains insights from a large amount of data.
It is safe to say healthcare is an ideal field for AI’s accelerating adoption. In fact, and already, the AI healthcare market has been expanding at a remarkable speed. According to G2, healthcare is one of the leading industries in terms of AI applications. A study in 2019 forecast a compound annual growth rate of 41.7%, and the market’s value will increase from $1.3 billion in 2018 to $13 billion in 2025.
Simultaneously, healthcare-related implementation of AI has attracted sizable investments. McKinsey reveals that in January 2020, the venture capital funding for the top 50 companies in AI applications in healthcare reached $8.5 billion. In the first quarter of 2020 alone, the field received a total of $635 million investment.
Delivery care is better in many ways, thanks to AI
Around the world, numerous healthcare-related activities are using AI. Among categories, patient care stands out with diverse possibilities.
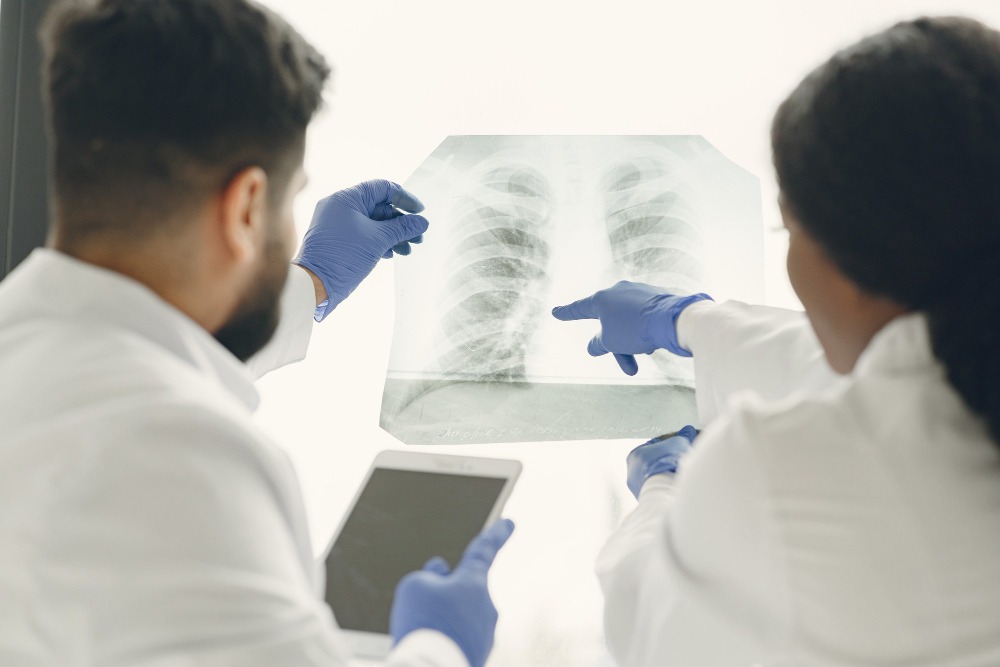
Better medical images to notice health conditions
Firstly, imaging.
Imaging is the practice of using computer vision to notice health conditions from medical images (X-rays, CAT scans, and MRIs). For doctors and clinicians, medical images are complicated to process because of:
- The high resolution
- A wide variety of possible objects
- The fact that a diagnosis requires careful analysis of multiple features.
To train AI systems for this task, they feed the machine with sample images. Based on these samples, the algorithm develops a neural network to identifies edges, curves and shapes signaling any abnormality. A study carried out by Case Western Reserve University in 2017 showed a deep learning network that could identify invasive forms of breast cancer from pathology images with an accuracy rate of 100%.
Therefore, we can safely assume AI is increasingly enhancing the productivity of radiologists and pathologists. It will provide vital support for their decision-making process and reduce the risk of human error.
Better patient engagement
Second, AI offers significant support in terms of patient engagement. Simply put, it is how well the institution responds to patients’ inquiries. Providers consider patients as healthcare consumers and their satisfaction matters.
Many institutions, therefore, have been interested in AI-enabled engagement tools that help deliver a personalized and convenient healthcare experience. For example, via an AI-enabled conversational interface (such as AI chatbots), the patient can inform the institution about their symptoms and get automated clinical guidance.
More than treating current patients, providers are looking to use AI to identify medical needs outside the hospital. An organization has employed AI to sift through data and identify people with a high risk of being infected with Covid-19. Then send targeted text messages that guide them to visit testing centers.
Additionally, AI technologies deliver better healthcare both remotely and within the hospital. On the one hand, they facilitate services relating to remote health (also known as telehealth). For example, doctors employ AI in monitoring a patient’s cardiopulmonary vital signs to generate early yet highly accurate cardiac and pulmonary diagnoses.
On the other hand, AI assists human clinicians during medical procedures. For instance, doctors can estimate blood loss in real-time during childbirth using computer vision to prevent the risk of delayed bleeding intervention.
Another example is employing AI to process input from bedside monitors to keep track of inpatients’ well-being and providing doctors with warnings.
Clearly, with AI, there is a prospect of enhanced care outcomes for patients and improved productivity, reduced pressure for professionals. It is safe to say the technology’s impacts are not only visible on patient care delivery but the industry as a whole. AI has become a new dynamic that continuously provides innovative and sustainable solutions to the complex system of modern healthcare.
ABOUT GEM
GEM offers dynamic AI-drive solution development to enable greater revenue and boosted productivity across industries. Our AI service list expands across four branches: Computer vision, Character recognition, Natural language processing, and Predictive recommendation systems. We leverage the power of AI to tailor scalable and efficient solutions that address your unique painpoints.
Don’t miss our latest updates and events – Follow us on Facebook and LinkedIn!