Contents
In today’s hyper-connected world, businesses are constantly seeking innovative solutions to stay ahead of the competition, optimize operations, and deliver exceptional customer experiences. In this pursuit, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a game-changer as it revolutionizes industries and transforms the way organizations operate.
Statistics have shown that AI adoption in businesses is growing rapidly, leading to significant improvement and tangible benefits.
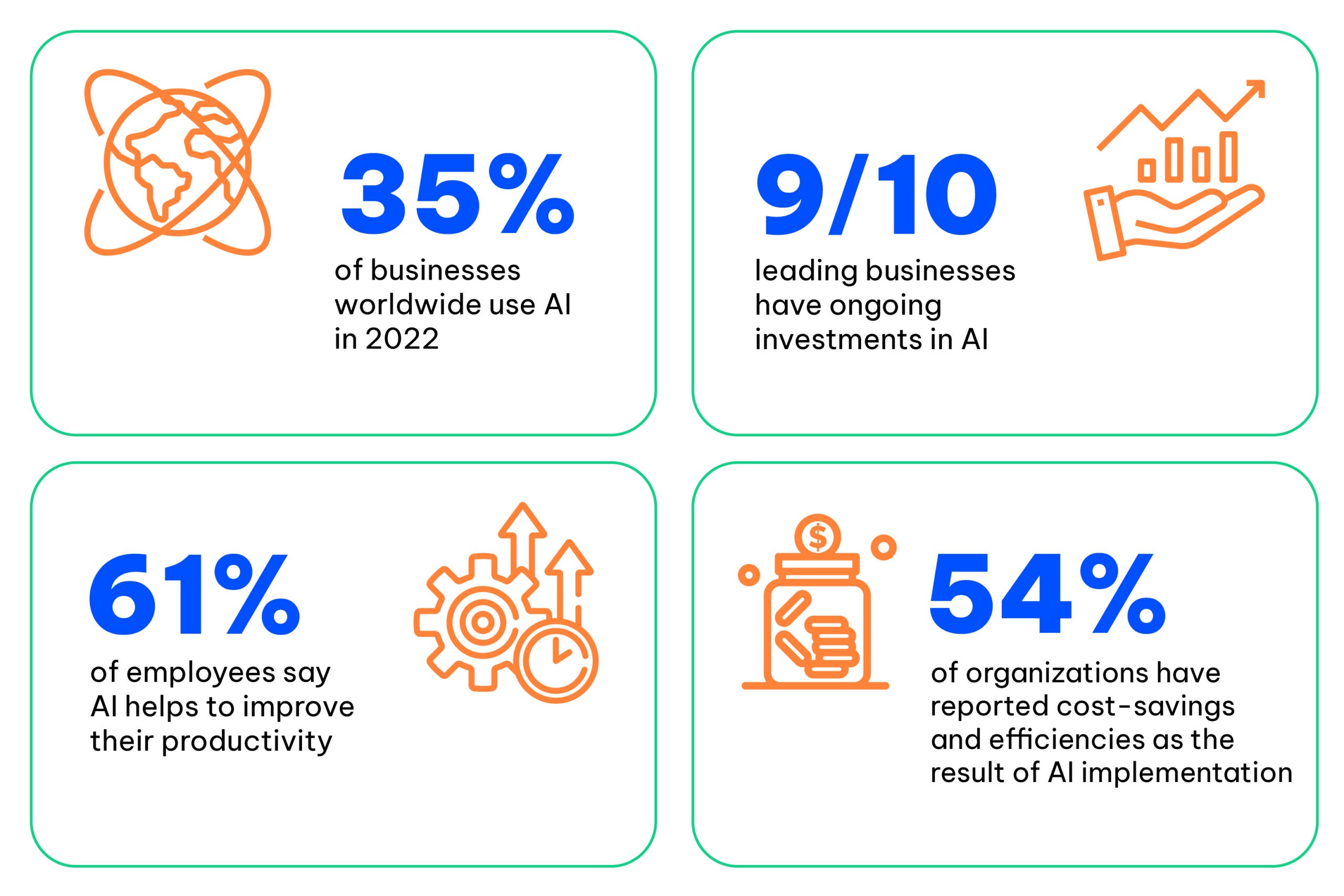
As AI adoption becomes increasingly prevalent, how can businesses get the best from their investment? How can they avoid wasting resources and money on ineffective projects?
GEM’s Complete Guide for AI Adoption in Businesses will help you navigate this journey toward AI-powered innovation. Let’s define what AI is and what values you can derive from it!
🚀 Ready to unlock the full potential of AI for your business?
Discover how AI Agency services by GEM Corporation can transform your operations, boost efficiency, and give you a competitive edge. Whether you’re looking to automate workflows, harness data, or build intelligent solutions—we’re here to help.
What is AI?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a sophisticated technology that uses real-time data to replicate human intellect and make real-time judgments. In other words, artificial intelligence is trained to think, behave, and respond like an actual, live human does.
AI, Machine learning, and Deep learning
The connections between the three terms can be confusing for beginners. Let’s clarify the ambiguity here.
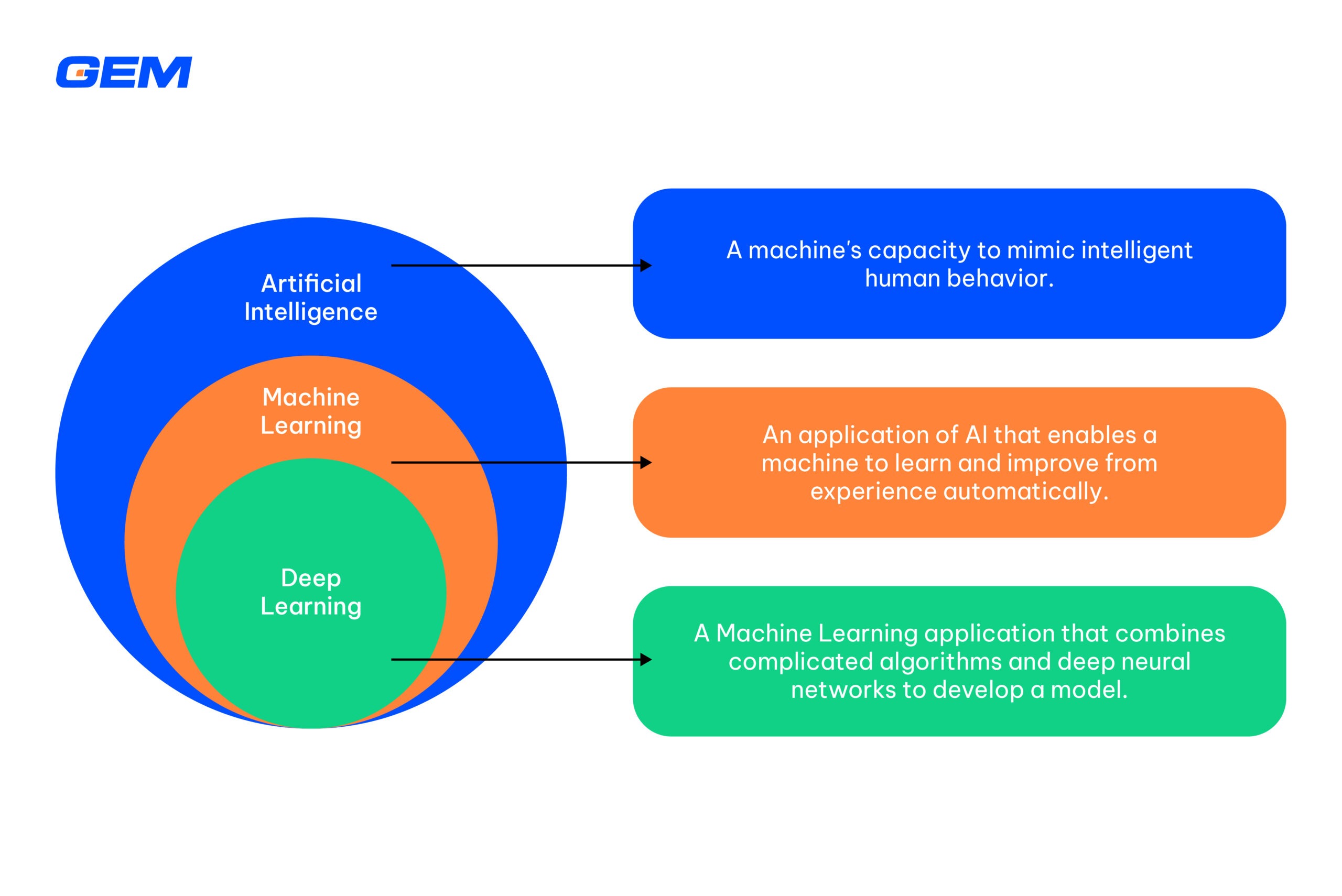
Artificial intelligence is the ability of computers to simulate human cognitive capabilities like processing information, reading texts, and interpreting patterns and trends.
Machine learning is a sub-field of artificial intelligence, founded on the idea that systems may learn independently from supplied data. Thanks to this remarkable learning ability, Machine Learning systems can perform particular repetitive tasks with minimal manual effort.
Deep learning is a method of developing and training neural networks to learn and create outputs that do not require supervision.
Read GEM’s guide on how you can tell Machine Learning and Deep Learning apart – in case the confusion still bothers you!
With this advanced technology, what practical values can you expect from AI adoption in businesses?
4 Benefits of AI Adoption in Businesses
Automating workflow
A workflow is defined as a set of actions or tasks that need to be completed to achieve a certain goal. Workflow automation is automating the steps of a chosen business process – be it approving requests, sending emails, or creating reports – via dedicated software or app solutions.

AI’s contribution to making the workflow more efficient lies in its ability to complete routine tasks. More and more business operations are automated with AI. For instance, as of now, ChatGPT is used in various business tasks: creating content, writing programming code, helping with customer onboarding, conducting research, and more.
Customizing customer experience
Customer service is among the fields where AI adoption in businesses thrives most rapidly. There are several ways AI helps businesses deliver a highly personalized experience to their customers, enhancing customer loyalty and satisfaction. We can name a few very popular examples:
- Segmentation of customers based on behaviors, demographics, and preferences
- Personalized recommendation of products and services
- Personalized messages, offers, and reminders
- Customized guidance
- AI-enabled chatbots or engines answer inquiries and complete simple requests

AI has the ability to understand, shape, and optimize the customer journey, yet all of this is only possible with strategic and at-scale analysis of customer data.
Therefore, AI urges businesses to gradually become “customer-first”. Harvard Business Review concluded that AI customization is nowadays about creating “positive moments” at every physical and virtual touchpoint throughout the customer experience.
Thorough market research
Market dynamics are largely influenced by consumer sentiment – the dissemination and quantification of which is challenging.
Nowadays, we’re living in a data-abundant world, where it is possible to explore not just the person’s age or gender, but also their political and social interests, professional aspirations, and so much more. The next challenge is to make sense of it with AI adoption in businesses.

As AI evolves, there is a growing number of tools and solutions for analyzing data and yielding insights. They can scan unstructured data (reviews, social media posts, and blogs) to identify patterns relating to customer behaviors. These insights help companies predict future trends and shape business development strategies and decisions. Market researchers can now dedicate their efforts to more complex tasks such as interpreting results and yielding actionable insights.
Fostering innovation
Innovation is the keyword to thrive in the current era which is full of disruptions and challenges – as noted by Ngo Khanh Hoang, GEM’s CEO, in one of his recent interviews.
The changes offered by AI adoption in businesses are beyond solving contemporary challenges. It urges businesses to be data-driven, collaborative, and open to changes. In the long run, these mindsets and working shifts ensure the company stays future-proof and adaptive.

Excited yet? Before executing an AI adoption plan to harness its potential, there are several questions you should keep in mind. To name a few:
- Are we properly ready to adopt an AI system?
- What should we do before, during, and after the implementation phase?
Explore how to get ready for such a massive change in this article of GEM about preparation for AI adoption in businesses.
Besides the benefits, there are also some challenges that businesses should be well aware of. Explore more about those challenges here!
Applications of AI in Businesses
AI has been making our lives simpler than ever before. Across industries, AI improves internal processes’ efficiency and enhances the services and products provided to customers.

Here are the popular use cases of AI adoption in businesses of different domains:
- Marketing and Customer Experience: Customer Segmentation and Targeting, Personalized Recommendations, Chatbots and Virtual Assistants, Content Generation and Optimization,…
- Operations and Supply Chain Management: Inventory Optimization, Quality Control and Defect Detection, Supplier Management and Risk Assessment, Warehouse Management,…
- Finance and Risk Management: Fraud Detection and Prevention, Credit Risk Assessment, Risk Analytics and Stress Testing, Financial Forecasting and Planning, Investment and Portfolio
- Healthcare and Life Sciences: Medical Imaging Analysis, Disease Diagnosis and Prediction, Precision Medicine, Drug Discovery and Development, Remote Patient Monitoring, Clinical Trial Optimization,…
- Manufacturing and Industrial Processes: Predictive Maintenance, Process Optimization and Automation, Product Design and Optimization, Autonomous Robots and Manufacturing Systems
Save Up to 45 % of Your Team’s Time with AI
Eliminate repetitive tasks, accelerate processes by up to 50 %, and redeploy your team on strategic initiatives.
6 Stages to a Successful AI Project Implementation
The fundamental obstacles to AI adoption in businesses have little to do with learning tools or code implementation. Instead, the most serious challenges stem from data-related issues since AI initiatives are primarily data-driven.
Therefore, a data-centric implementation approach is needed, and one well-known example is the Cross-industry Standard Process for Data Mining (CRISP-DM) methodology.
CRSIP-DM emphasizes an iterative approach to data-intensive processes. The entire method creates a cyclic iterative loop, resulting in continuous data modeling, preparation, and evaluation.
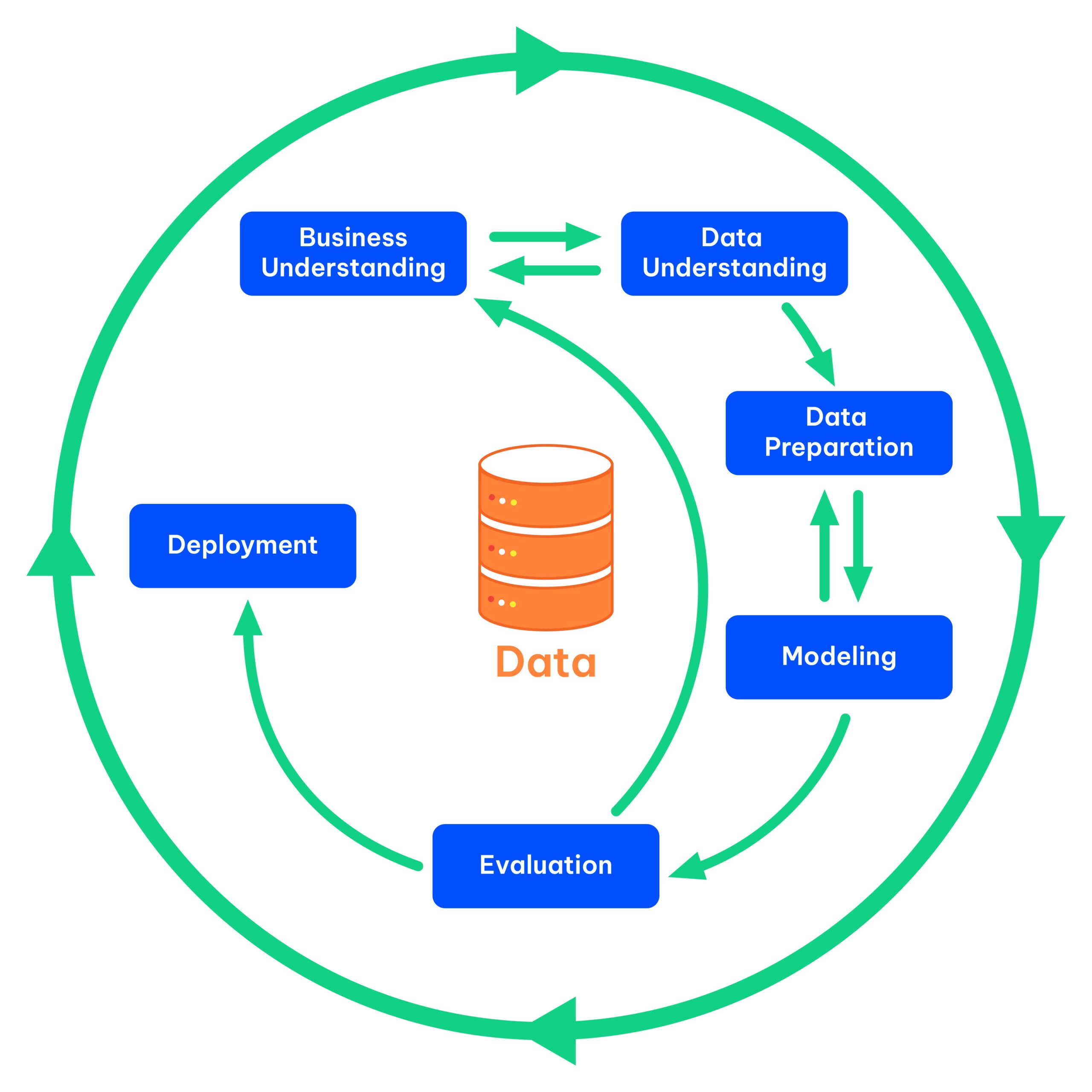
Business Understanding
The first vital step of AI adoption in businesses is business understanding, which consists of turning business challenge(s) into a quantifiable goal and then smaller tasks. The project’s success depends heavily on how the key stakeholders understand their business – its current performance, its tech infrastructure, what problems it is facing, and what AI use case to adopt.

Below are the 4 main tasks you need to do in this stage:
- Determine business objectives: First, you need to properly comprehend what the customer truly wants to achieve from a business standpoint before establishing business success criteria.
- Assess the situation: Determine resource availability, project requirements, risks, and contingencies, and conduct a cost-benefit analysis.
- Define data mining goals: Clarify the goals to achieve with data mining.
- Plan for project execution: Create a plan that defines how many phases there are, as well as the tools and techniques needed.
Data understanding
The second step of AI adoption in businesses emphasizes finding, acquiring, and evaluating to make sure the collected datasets can give meaningful answers to a specific business use case.
- Gather preliminary data: Gather data and (if necessary) import it into the analytic program
- Describe the data: Examine data and note its surface attributes such as data format, number of records, and field identifiers.
- Investigate data: Investigate data further to discover correlations
- Check the data quality: Evaluate data quality and document any detected issues.
- Create a project plan: Choose the suitable tools and create a precise plan
Data Preparation
In this phase of AI adoption in businesses, data is transformed and cleaned to meet standards. A general rule of thumb is that data preparation takes up 80% of the project’s effort. There are many aspects of data preparation:
- Case weighing
- Feature engineering
- Missing data imputation
- Data reformatting to fulfill technical requirements

Five main tasks that need to be done in this stage of AI adoption in businesses are:
- Select data: Decide which data sets will be utilized and justify exclusion/inclusion.
- Clean data: Enhance data quality to the required level – and it is usually the most time-consuming task. Without it, you’re likely to have garbage-in, garbage-out. During this task, data experts will rectify, impute, or eliminate erroneous values.
- Construct data: Add additional information and/or make changes to existing information to support the analysis process. This can be done by either creating derived attributes or generating entire new records. For example, one’s height and weight are variables to calculate their body mass index (BMI).
- Integrate data: Create new data sets by merging information from several sources.
- Format data: Reformat data to conform to the modeling tool’s specifications. For example, you might transform text values containing integers to numeric values to execute mathematical operations.
Modeling
Modeling is the shortest and also the most exciting stage of any project of AI adoption in businesses. Based on different modeling techniques, you’ll build and assess various models. This stage has four tasks:
- Determine modeling techniques: Choose which algorithms to test (for example regression or neural net).
- Generate test design: Divide the data into training, testing, and validation sets depending on your modeling technique.
- Construct model: Execute a couple of lines of code such as “reg = LinearRegression().”fit(X, y)”.
- Evaluate model: Evaluate the results of different models based on domain expertise, pre-defined success criteria, and test design to choose the most suitable one.
Evaluation
During the previous phase, the project team focuses more on technical criteria. In this next phase, they will examine the model’s compatibility with the company.

Furthermore, they will review documents to see how well the process of AI adoption in businesses went.
- Evaluate results: Do the models fit the requirements for company success? Which one(s) to choose for the company?
- Review procedure: Examine the project to see if it has been properly completed. Was anything left out? Were all steps followed correctly? Summarize results and make any necessary corrections.
- Determine next steps: Determine whether to deploy, iterate further, or start new projects based on the prior tasks.
Deployment
The final stage is to deploy the model. Depending on the objectives of AI adoption in businesses, this step might be as easy as creating a report or as sophisticated as deploying a repeatable data mining process across the company.

A model’s value isn’t apparent until the consumer has access to its outcomes. This phase’s complexity varies greatly. This phase consists of four tasks:
- Plan the model’s deployment: Create and outline a plan for deploying the model.
- Plan monitoring and maintenance: Create a detailed monitoring and maintenance plan to avoid problems throughout a model’s operating period (or post-project phase).
- Make a final report: The project team creates an overview of the project, which may contain a summary of the data mining findings.
- Evaluate the project: Conduct a project review to determine what went well, what might have been improved, and how to make modifications in the future.
Imagine What You Could Achieve with AI Streamlining Your Operations
Transform your operations with precise, AI-driven workflows. From reducing errors to improving speed, achieve operational excellence and drive sustainable growth.
Trends of AI adoption in Businesses
Analysts predict that as AI adoption in businesses expands, it will take on additional roles and alter the landscape of numerous industries. Companies have successfully implemented proofs-of-concept and deployed AI in production. Some companies have even operationalized their AI and machine learning strategy, with projects spreading across the company and best practices and pipelines in place.

Let’s take a look at the rising trends of AI adoption in businesses.
Creative/Generative AI
Generative AI models can learn the properties and patterns of data to perform creative tasks that used to be done by humans only. The possibilities range from creating text, images, and videos in various styles to generating personalized content. Therefore, thanks to generative AI engines, AI adoption in businesses allows machines to perform creative tasks that were only performed by humans.
Some generative AI examples are:
Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3 (GPT-3) is a language forecasting model developed in 2020 that autocompletes text after researching millions of online pages and scientific articles on the Internet. GPT-3 contains 175 billion machine learning parameters.
Powered by contemporary copywriting techniques, GPT-3 produces human-like written material after being fed settings like subjects, descriptions, or introductory phrases. You may use this tool to create outlines, summaries, essays, op-eds, and other documents.

DALL-E is a deep learning model created by OpenAI. You can produce art using DALL-E by typing in a description, and DALL-E will generate numerous variants. You can also use text prompts to build a new picture from an existing one. Users can do “in-painting” or delete elements of an image and replace them with something else.
With DALL-E, those involved in AI adoption in businesses may also do “out-painting,” meaning DALL-E adds extra to an existing photograph (primary topic or scenery). DALL-E’s qualities make it a useful tool for the branding and creative marketing industries.
Democratization: low-code, no-code AI
As a new trend of AI adoption in businesses, low-code and no-code AI platforms are intended to make the process of developing and distributing software applications easier by reducing the need for human coding.

These platforms offer a graphical user interface that lets users construct programs by dragging and dropping pre-built components, hence automating much of the development process. This method dramatically decreases the time and resources needed to construct apps, allowing non-technical individuals to design bespoke solutions without extensive programming experience.
66% of developers are either utilizing low-code, no-code tools (39%) or intend to do so (27%) in 2023 as it is 70% cheaper and has a faster completion time (it can be as fast as three days) compared to traditional methods. By 2026, developers outside formal IT departments will make up at least 80% of users of low-code development tools, up from 60% in 2021, according to Gartner.
Greater AI-human collaboration
The scope of AI adoption in businesses regarding taking up human activities will reach unprecedented heights, earning them the name cobots or collaborative robots. Market insiders predict that more organizations will adopt machines with built-in AI to perform repetitive and physically demanding activities.
This collaboration allows human personnel to do more specialized tasks. AI adoption in businesses, hence, can also help teams discover and respond to problems or breakdowns quickly, enhancing safety and minimizing repair or injury costs.
- Healthcare and hospitality: Sample collecting, surgery, health supplies stocking, nursing for the disabled or elderly.
- Automotive manufacturing: spray painting, automobile assembly, spray painting, system testing, surface polishing and modifying, and rebuilding car assembly lines to accommodate electric models.
- Agriculture: drones for seed sowing, fertilizer and pesticide application, trespasser and invasive species detection, and indoor farm LED lighting and hydroponics
- Food and Beverage: food packaging, warehousing
Find the AI Solution That Fits Your Business Perfectly
Confused about the right AI approach? Let us help you uncover a solution tailored to your goals and challenges.
Conclusion
Undoubtedly, AI adoption in businesses has yielded significant benefits for businesses. It transforms how organizations operate, reduces human errors, and improves decision-making. Therefore, it is clear that adopting AI helps businesses to scale up tremendously and gain a competitive advantage.
Drive innovation and efficiency with GEM’s AI services
What do you think about partnering with a savvy provider of AI development and consulting services to optimize the AI-driven value your business can harness?
With a proven track record of many successful projects that delivered real-life impacts in terms of productivity and revenue growth, GEM is the one who will level up your AI adoption journey.
Connect with our AI experts via the form below and let’s see how the technology will empower your business.