Contents
AI is paving the way for a major tech-driven shift in the insurance industry, and it is time for businesses to embrace this change.
Artificial intelligence (AI) can be understood as the recreation of human intelligence in machines, allowing them to make decisions and carry out tasks like humans.
The key to perfecting AI solutions lies in training them with more quality data input, while insurance is one sector that quickly generates data in great volumes. Therefore, employing AI in insurance is no longer a vision of the future – its impacts are already very apparent for insurers.
Understanding the transformational role of AI in insurance
Since the insurance industry was formed, data has been its core dynamic. The global surge in data means a heavier workload on insurers, who still need to comply with regulations, go through various manual paper-based procedures, and ensure a high level of accuracy in their performance.
As a result, the integration of AI technology has been accelerated to reap practical benefits. With AI in insurance, businesses can automate labor-intensive duties, reducing operative costs and increased efficiency. AI may help save $390 million across their front, middle and back offices by 2030. Furthermore, it facilitates analytics to help businesses understand their customer base better and customize their service and marketing approaches. Also, AI plays a vital role in strengthening security and ensuring compliance.
In short, with AI, insurance companies will function faster, with fewer costs and more safety.
How is AI being used by insurers around the world?
McKinsey estimates that, for the sector, AI-powered functions and use cases will generate a potential annual value of up to $1.1 trillion. Specifically, how has AI technology been translated into real-life values?
1. Claim processing
Human staff can be highly prone to errors while performing investigation, review, adjustment, all of which are parts of claim processing. They also need to deal with customers’ varying, unstructured data formats while adhering to constantly changing regulations. Furthermore, many companies struggle to spend wisely, as they have to hire more personnel to handle the enormous workload.
With AI in insurance, companies process large amounts of information quickly and many assignments will be automated. The time needed to complete case-solving will be reduced from several days to hours or even minutes, and the hiring spend will decrease as well.
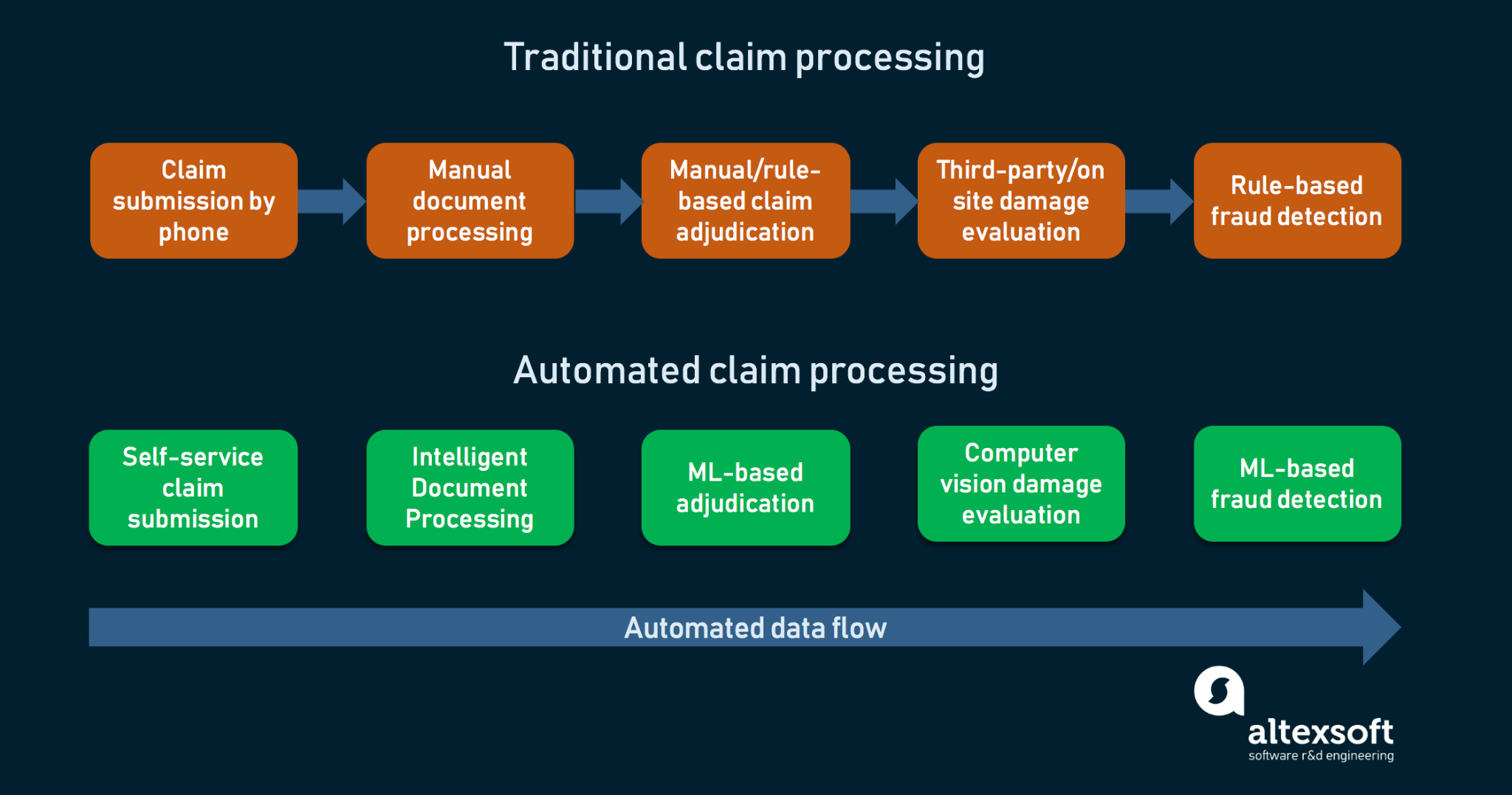
For example, an insurance firm in Japan has employed an ML-based system that scans thousands of medical certificates before calculating payouts based on the length of patients’ hospital stays, medical history, and surgical procedures. This move led to a 30% increase in productivity, and the payout accuracy rates also improved.
2. Inspection
In the US, compared to a typical construction worker, property adjusters are almost four times as likely to have an injury. To minimize the risk, AI in insurance will take over several labor-heavy and potentially dangerous inspection tasks, especially when it comes to properties and vehicles.
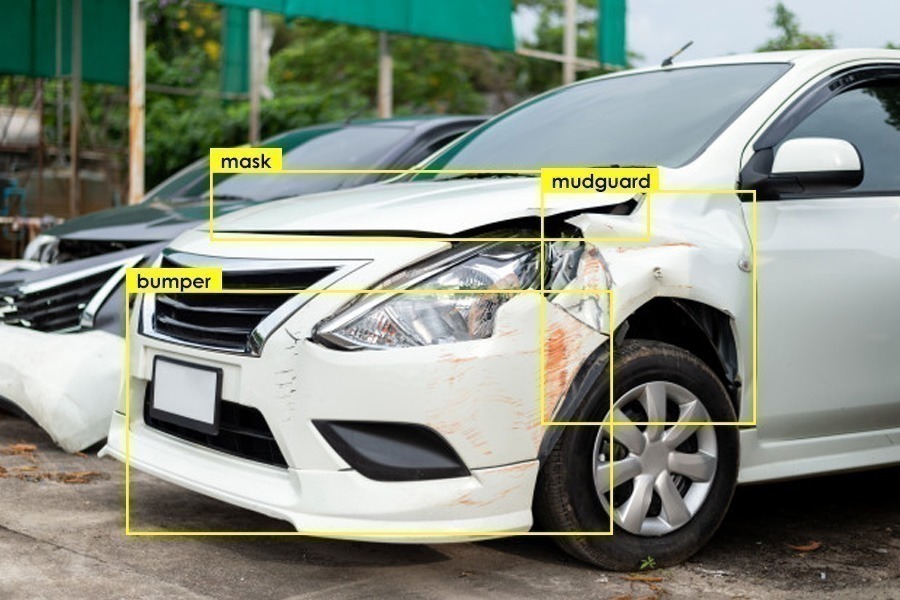
Property adjusters can use drones or cameras equipped with computer vision to assess roof damage and estimate repair costs. The same technique can be used to inspect industrial equipment, fields, crops, etc., that are affected by natural disasters.
AI in insurance can also gather data from multiple sources, including IoT datasets (temperature, pressure, object position…) and geospatial data from satellites, to form a holistic picture of the situation and generate more accurate conclusions.
For example, a Japanese auto insurer has employed an AI-based computer vision system to examine damaged vehicles. They hope to shorten the time needed to determine repair costs considerably using this technique instead of the conventional method that takes up to two or three weeks.

2. Fraud detection and prevention
Non-health frauds alone cost insurers more than $40 billion per year. However, outdated rule-based systems, which are still largely used, cannot effectively spot advanced fraud schemes. In this case, AI in insurance overcomes the shortcomings of previous methods by detecting any abnormality and false information that is leveraged to get a bigger claim payout. Furthermore, AI-powered systems will run fast, automatic background checks on individuals and businesses to calculate the risks associated with them.
For example, a Turkish insurer saw remarkable improvements after switching from manually reviewing claims of fraud, which used to take up to 2 weeks, to an AI-based predictive fraud detection system. They realized an impressive 210% return-of-investment and saved over $5.7 million in costs for fraud detection and prevention thanks to leveraging AI in insurance.
3. Underwriting
When it comes to the underwriting process, rule-based evaluation and risk engines no longer suffice to provide accurate estimates. Especially, insurance scenarios are getting more complex (e.g, usage-based insurance pricing for shared assets), and fraud levels are becoming more elaborate.
Thanks to computer vision and IoT data, solutions based on AI in insurance can offer substantial assistance for insurers in keeping track of the asset state and making timely adjustments. For example, a company built a machine-learning model to predict the risk of flooding in an area, using historical and geospatial data inputs from digitized documents. The model helped reduce throughput time tenfold.
4. Document digitization
The rapid digitalization of documents is performed by OCR, short for optical character recognition, which converts handwritten or printed text inputs into machine-readable text data.
Since insurance tasks still largely rely on paper-based data formats, AI in insurance will be a game-changer by drastically accelerating processes and improving efficiency. Printed and hand-written documents will be scanned to capture essential information and translated into digital input.
An insurance firm based in France developed an OCR system for extracting data from unstructured scanned documents and submitting it for further analysis, achieving an accuracy rate of 96%.
5. Customer care
AI in insurance help reimagine how customer care is executed. For example, simple queries will be automatically handled by chatbots, while more complex ones will be forwarded to human employees. Additionally, affective computing, an AI-based technique, can understand clients’ feelings and trigger actions to ensure their satisfaction, such as directing their call to a more experienced live agent when the system senses their frustration.
AI in insurance not only mean faster replies, but they also imply time and cost efficiency, together with a better reputation. For example, they helped a South African insurance company lower cost per transaction by 91%, save 2000 hours of processing time per month, and improve customers’ positive sentiments.
6. Personalized marketing and offerings
AI in insurance can aggregate meaningful details about customers from disparate datasets, helping companies comprehensively understand current and incoming interests and trends. These factors are beneficial for customer profiling to realize personalized service and pricing.
For example, an insurance company has learned that customers usually start looking for better deals when their policies are about to expire, with only 53% choosing to stay with their current provider. With this information, they consider renewal time to be a critical stage for engagement and retention. Therefore, they will send automated renewal notifications with discounts to ensure the customer will not turn to a competitor.
The outlook for the employment of AI in insurance
According to a survey done by PwC, cyber security and privacy threats were regarded as the main risks associated with AI solutions by respectively 42% and 36% of respondents. However, PwC argues that the main obstacle is, in fact, the lack of specialized skills and workforce to properly manage the technology.
Another challenge is silos, meaning business lines and analytics groups fail to work jointly to provide AI systems with sufficient data to produce the desired outcomes.
Therefore, to realize the potential of AI in insurance, businesses must be well prepared for what it will take. They will need clean, standardized datasets to train the models, AI talents to build advanced algorithms, and sufficient technology infrastructure to support the shift to AI. Moreover, they will have to adopt an innovative approach to governance and operation. The preparation will be sophisticated yet extremely necessary to build a solid foundation for their prospective success.
Closing thoughts
AI in insurance has already started to bring about positive changes: cutting costs, speeding up processes, and improving service efficiency, thus benefiting insurers and consumers alike. While it is not easy to successfully integrate AI into the workflow, the technology still proves to be a powerful tool to stimulate long-term growth and prosperity.
Are you looking for an AI developer?
1. GEM Corporation is an IT Outsourcing company experienced with developing AI solutions. We have worked on developing NLP and OCR solutions for top industrial corporations in Japan; specialized in deploying chatbots, text and image processors, recommendation systems. We are also partnering with Vietnam National University’s AI Laboratory on scientific research and talent training.
2. Our domain expertise includes Logistics, Telecommunications, Finance, Banking and Insurance, Retails, Manufacturing, and so on.
3. We have more than 7 years of experience. Our offices are based in Hanoi, Vietnam and Tokyo, Japan.
4. We have successfully built more than 100 successful projects for our clients in the US, UK, Europe, Japan, Korea, Singapore, and many more.
5. Let us know how we can help you build your next AI solution. Contact us now and get a demo for your project.