Contents
- Understanding the ITSM Landscape
- What is ServiceNow ITSM?
- What are the ServiceNow ITSM modules?
- Benefits of ServiceNow ITSM
- How to Measure ITSM Performance?
- Implementing ServiceNow ITSM: A Phased Approach
- Integrating ServiceNow with Your IT Ecosystem
- Optimizing ServiceNow ITSM for Long-Term Impact
- How to Choose the Right ServiceNow Partner?
- GEM Corporation – Your Reliable ServiceNow Solution Partner
- Conclusion
ServiceNow ITSM offers a structured way to manage IT services across complex environments. From core modules like incident and change management to advanced capabilities in workflow automation, the platform supports consistent, data-driven operations. In this article, we’ll look at the key components of ServiceNow ITSM, how it’s implemented, what metrics matter, and where integration plays a role in long-term performance. We’ll also cover practical steps for optimization and selecting the right solution partner. Let’s break down what it takes to make ServiceNow ITSM work in real-world enterprise settings.
Understanding the ITSM Landscape
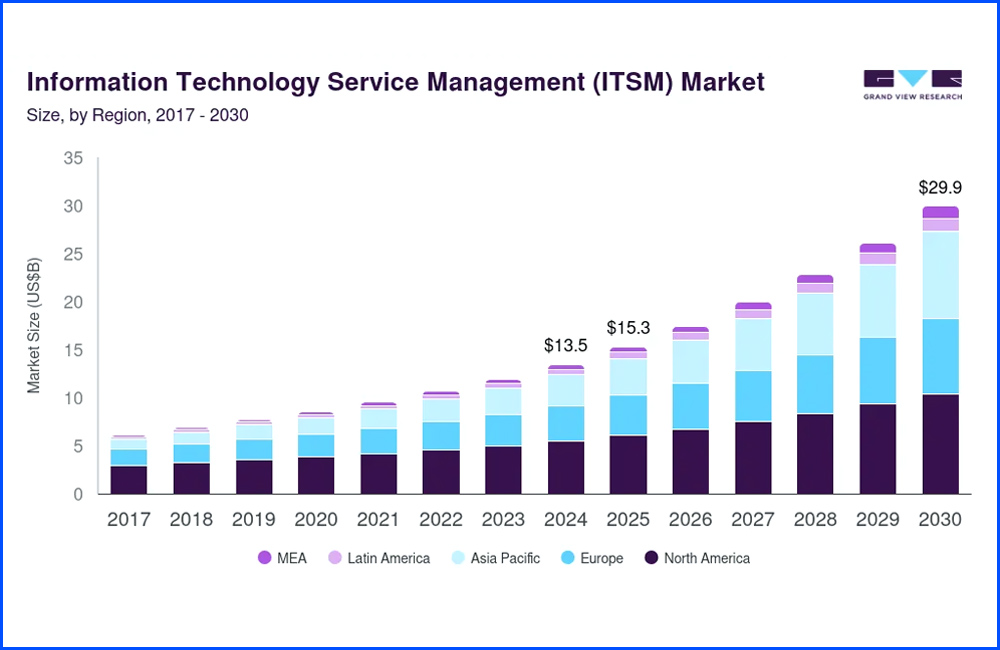
(Source: Grandview Research)
The global IT Service Management (ITSM) market is undergoing steady expansion, with market size projected to reach USD 29.9 billion by 2030, more than doubling from its 2024 valuation. This trajectory reflects the impact of cloud migration, hybrid environments, and evolving regulatory frameworks on enterprise IT operations. As infrastructure grows more distributed and service expectations rise, ITSM platforms have become foundational to managing complexity at scale.
Organizations are deploying ITSM solutions to streamline workflows, improve service quality, and meet compliance demands. From automating incident handling to enabling audit-ready documentation, ITSM tools now play a broader role in aligning IT functions with business needs.
ServiceNow ITSM is one of the core solutions driving this shift. Built on a unified architecture, it supports structured service delivery, cross-functional integration, and visibility across the service lifecycle. We’ll learn more about ServiceNow ITSM in the following sections.
What is ServiceNow ITSM?
ServiceNow ITSM (IT Service Management) is a cloud-based platform designed to standardize, automate, and streamline the delivery of IT services across an organization. It provides a centralized system for managing incidents, problems, changes, and requests, helping IT teams shift from reactive firefighting to proactive service delivery. Its core purpose is to bring consistency and efficiency to IT operations while aligning services with business needs.
For enterprises under pressure to scale digital operations, ServiceNow ITSM supports broader IT strategies by connecting service management with infrastructure, security, and business workflows. It integrates data, processes, and teams through a unified platform, making it easier to manage service portfolios, track performance, and improve response times. With built-in AI and real-time analytics, it also helps teams identify bottlenecks and optimize service delivery.
While traditional ITSM platforms often rely on siloed tools and manual processes, ServiceNow offers a modern architecture that supports end-to-end service visibility and automation at scale.
Its adoption across industries reflects this shift – ServiceNow ITSM is recognized as the top ITSM tool by G2 (ServiceNow). This milestone signals how organizations are increasingly investing in platforms that support agile, connected, and data-informed IT service models.
What are the ServiceNow ITSM modules?
ServiceNow ITSM is built around a modular structure that supports core ITIL processes through a unified, cloud-based platform. Each module addresses a specific area of IT service management, contributing to more structured workflows, better visibility, and consistent service delivery. Below is an overview of the key modules and their role in enterprise IT operations.
CSDM – Common Service Data Model
CSDM provides a standardized approach to structuring and relating data within the Configuration Management Database (CMDB). It supports alignment between IT services and the infrastructure that delivers them, creating a shared data foundation across ServiceNow modules.
- Defines service models that link business services to technical components
- Supports consistent data relationships for change, incident, and problem workflows
- Improves accuracy in root-cause analysis and service impact assessments
- Enables unified reporting across ITSM, AIOps, and asset management functions
Incident Management
Incident Management focuses on restoring normal service operations as quickly as possible after a disruption. It provides structured workflows for logging, categorizing, prioritizing, and resolving incidents.
- Centralized incident tracking with automated routing and escalation
- SLA tracking to align response times with business expectations
- Integration with knowledge base for faster resolution
- Real-time dashboards for incident volume, trends, and resolution times
Problem Management
Problem Management addresses the root causes of recurring incidents. It complements incident workflows by identifying systemic issues and preventing future disruptions.
- Root cause analysis tools to investigate recurring problems
- Known error database for faster resolution of familiar issues
- Structured workflows for problem detection, diagnosis, and resolution
- Links to change management for implementing permanent fixes
Change Management
Change Management provides governance over changes to systems, applications, and infrastructure – balancing innovation with operational stability.
- Change request workflows to assess, approve, and schedule changes
- Integration with CAB (Change Advisory Board) for high-impact decisions
- Change calendar for visualizing upcoming changes and potential conflicts
- Automated risk scoring based on historical data and service dependencies
Release Management
Release Management supports the planning and coordination of application and infrastructure releases. It helps align delivery efforts with business timelines and quality expectations.
- End-to-end workflows covering build, test, deploy, and support
- Integration with DevOps pipelines for faster and traceable deployments
- Visibility into release readiness, compliance, and rollback planning
- Coordination across teams to reduce delays and post-release issues
Service Level Management
Service Level Management tracks and governs service performance based on defined SLAs. This module helps IT teams meet their commitments and improve user satisfaction.
- SLA definitions based on service tier, incident type, or user group
- Real-time monitoring of SLA compliance
- Automated breach alerts to support timely interventions
- Historical reporting to identify trends and performance gaps
Continuous Improvement Management
This module connects ongoing service improvements with broader business objectives. It provides tools to identify, execute, and measure improvement initiatives across IT operations.
- Aligns improvement efforts with strategic goals and key performance indicators
- Tracks progress through structured plans and performance dashboards
- Promotes accountability by assigning owners and deadlines to improvement tasks
- Encourages a culture of operational refinement through data-driven reviews
Configuration Management
Configuration Management maintains an accurate inventory of IT assets and their relationships across systems and services. It provides the foundation for change impact analysis, incident resolution, and compliance reporting.
- Manages configuration items (CIs), including hardware, software, networks, and documentation
- Establishes relationships between components to support service mapping and root-cause analysis
- Enables traceability of changes and system dependencies
- Supports governance through audit trails and lifecycle status tracking
Request Management
Request Management handles user-initiated requests for standard services, including hardware provisioning and access changes. This module helps streamline fulfillment while improving transparency and efficiency.
- Offers a unified service catalog with predefined request types
- Automates approval and fulfillment workflows to minimize manual effort
- Tracks request status to keep users informed throughout the process
- Supports reporting on request volume, time to resolution, and fulfillment trends
Knowledge Management
Knowledge Management provides a structured approach to capturing, organizing, and distributing IT knowledge across the organization. It supports faster incident resolution, better decision-making, and improved self-service adoption.
- Maintains a centralized knowledge base with articles, FAQs, and best practices
- Integrates with incident and request workflows to surface relevant content
- Enables article feedback and usage analytics to improve knowledge quality
- Supports content lifecycle management, including review and retirement workflows
Workflow and Talent Management
This module focuses on aligning people and processes within IT service delivery. It enables structured workflows and ensures that roles and responsibilities are matched with individual skills and business priorities.
- Maps tasks and approvals to defined roles and team structures
- Supports resource planning based on skill sets and capacity
- Promotes accountability through ownership assignment and escalation paths
- Helps identify workforce gaps and inform upskilling or hiring initiatives
Benefits of ServiceNow ITSM
ServiceNow ITSM supports a structured, data-driven approach to managing IT services across the enterprise. Check out the key benefits organizations can expect from a well-executed ServiceNow ITSM deployment.
- Deliver consistent, scalable service experiences
ServiceNow provides a unified platform for managing incidents, requests, changes, and problems. With standardized workflows, SLA tracking, and embedded knowledge management, service delivery becomes predictable and repeatable across business units and locations, reducing fragmentation and improving scalability.
- Improve IT service responsiveness and efficiency
Automation of routine actions, such as ticket categorization, routing, and resolution, reduces manual workload and shortens response times. Real-time dashboards and performance analytics help IT teams prioritize tasks and address service disruptions proactively, improving both speed and accuracy without increasing headcount.
- Break down silos across service functions
ServiceNow aligns ITSM processes with other enterprise functions, such as HR, facilities, and security, through a shared data model and integration-ready architecture. This allows cross-functional workflows to run seamlessly, ensuring end-to-end visibility and a smoother experience for employees and service agents.
- Use AI to accelerate triage and resolution
Embedded AI capabilities support faster classification, intelligent routing, and predictive recommendations. Virtual agents handle common inquiries, while analytics detect recurring issues and suggest next-best actions. These tools help streamline service desk operations, particularly in high-volume environments.
- Improve employee experience with self-service and omnichannel access
ServiceNow offers multiple access points – web portals, chatbots, and mobile apps, so users can submit requests, track progress, or find answers on their own. This always-on access reduces dependency on support teams and improves satisfaction by setting clearer expectations and shortening wait times.
- Support strategic alignment and IT modernization
ITSM serves as a launchpad for broader digital transformation by increasing process visibility and automation. Integration with CMDB, ITOM, and other modules allows IT teams to shift from reactive support to proactive service delivery, aligning IT operations with strategic business priorities.
Collectively, these benefits position ServiceNow ITSM as a foundational platform for organizations looking to scale IT operations while improving service quality, user experience, and operational agility.
How to Measure ITSM Performance?
Quantifying ITSM system performance requires a combination of operational and user-centric metrics. According to GEM’s experts, here are the 7 key metrics that offer a structured view of ITSM effectiveness.
Service Availability
This metric reflects the percentage of time a service remains accessible to users. Higher availability signals operational stability and reduces business disruption. It’s commonly tracked against service-level commitments and provides insight into infrastructure reliability.
Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR)
MTTR captures the average duration from when an incident is logged to when it’s fully resolved. A lower MTTR indicates faster recovery and more responsive support processes. It’s often used to assess the efficiency of incident workflows and identify delays in root-cause identification.
First-Contact Resolution Rate
This measures the proportion of incidents or requests resolved during the first interaction, without the need for escalation or follow-up. A high rate suggests effective frontline support and helps minimize ticket volume, improving both user experience and operational load.
SLA Compliance Rate
This metric tracks the percentage of service requests and incidents resolved within agreed timeframes. Consistent SLA performance signals process maturity and reinforces accountability. It also highlights gaps in capacity planning, priority management, or escalation logic.
Agent Throughput and Utilization
Agent throughput measures the number of tickets resolved per support agent within a given timeframe. When combined with utilization data, such as time spent per request or idle time, it provides insight into workload distribution and staffing efficiency.
User Satisfaction (CSAT)
CSAT is gathered through user feedback on specific service interactions. It reflects how well the service met expectations and provides qualitative input for improvement. High CSAT scores often correlate with faster response times, clear communication, and effective resolution.
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
NPS gauges user loyalty by asking how likely individuals are to recommend IT services to others. This metric moves beyond transactional feedback to capture overall sentiment about the IT organization’s value. It supports long-term planning by identifying promoters, passives, and detractors.
These metrics form a comprehensive framework for evaluating ITSM performance. They inform operational decisions, guide resource allocation, and support continuous service improvement across the enterprise.
Read more: Discover proven problem-solving strategies in ServiceNow that drive proactive root-cause resolution and operational resilience.
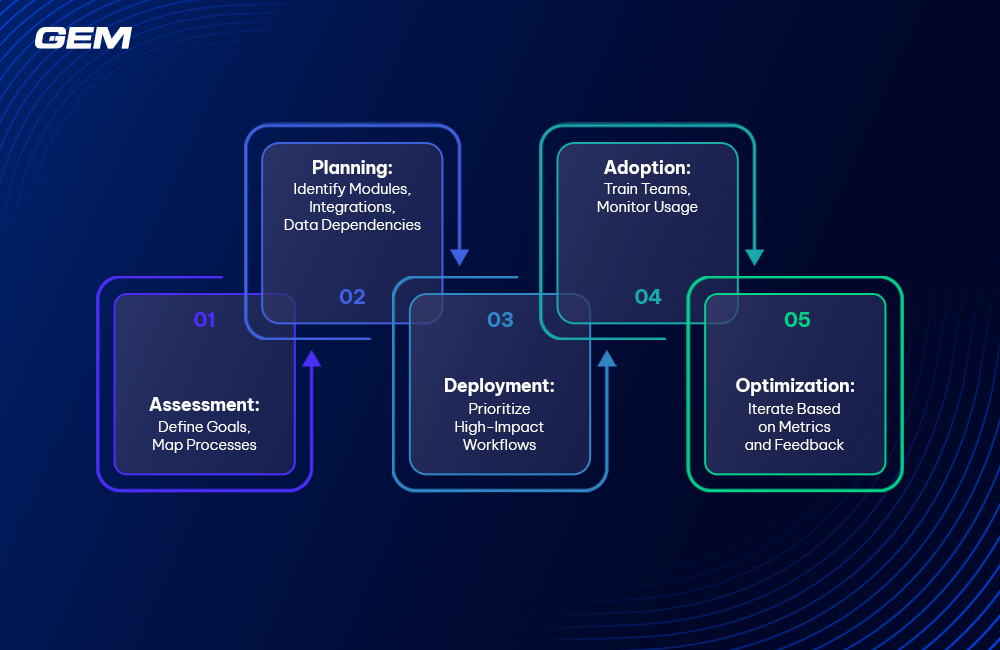
Implementing ServiceNow ITSM: A Phased Approach
Deploying ServiceNow ITSM calls for structured execution across multiple phases to align with business priorities, reduce operational friction, and accelerate time to value.
1. Assessment: Define Goals, Map Processes
The implementation begins by evaluating the current state of IT service delivery. This phase focuses on building a clear understanding of business objectives, service management maturity, and process gaps.
- Identify key stakeholders across IT, operations, and business units
- Define strategic goals for ITSM, such as improving SLA performance, cutting incident backlogs, or supporting a hybrid workforce
- Map existing service processes (incident, change, request, etc.) to pinpoint inefficiencies or non-standard practices
- Assess toolsets currently in use and determine what needs to be replaced, integrated, or retained
- Review compliance or regulatory requirements that may affect configuration or data storage
Deliverables from this phase typically include a current-state analysis, future-state vision, and a prioritized list of transformation targets.
2. Planning: Identify Modules, Integrations, Data Dependencies
Once goals and process maps are in place, the next step is to define the technical and functional scope of implementation. This includes selecting the ServiceNow ITSM modules to be deployed and outlining integration points.
- Select ITSM modules based on organizational needs – e.g., Incident, Problem, Change, Request, Knowledge, and CMDB
- Document dependencies between modules and other enterprise systems (Active Directory, monitoring tools, HR systems, etc.)
- Design a data migration plan for importing configuration items, historical tickets, and user profiles
- Define governance models for access control, role management, and approval chains
- Create a phased rollout roadmap aligned with business cycles and resource availability
This phase results in a detailed implementation plan, including timelines, resource assignments, and risk mitigation measures.
3. Deployment: Prioritize High-Impact Workflows
Deployment focuses on configuring selected ITSM modules and putting the platform into action. The emphasis is on delivering tangible value early by launching high-impact workflows first.
- Configure core modules and workflows in alignment with mapped processes and compliance standards
- Implement the CMDB with a focus on accuracy, relationships, and service mapping
- Automate routine workflows, such as ticket routing, approvals, and escalations, to reduce manual effort
- Test integrations with enterprise systems to validate data flow and performance
- Run pilot deployments with select teams or business units to gather feedback and iron out issues
Deployment is iterative by design, with each wave increasing platform reach and operational depth.
4. Adoption: Train Teams, Monitor Usage
Technology deployment alone does not guarantee success. Adoption requires a deliberate effort to prepare teams, encourage usage, and build trust in the platform.
- Conduct role-based training sessions for service desk agents, change managers, and team leads
- Develop user guides and knowledge articles tailored to internal processes
- Launch internal campaigns to raise awareness of new capabilities and self-service options
- Monitor usage patterns through dashboards and user analytics to identify adoption bottlenecks
- Set up feedback loops with frontline teams to surface usability issues and unmet needs
Early wins and visible improvements in service delivery help build momentum and strengthen platform adoption.
5. Optimization: Iterate Based on Metrics and Feedback
Once the platform is active and in use, the focus shifts to refining workflows, closing performance gaps, and expanding value through new use cases.
- Track key performance indicators such as SLA compliance, MTTR, first-contact resolution, and CSAT
- Use analytics to identify process inefficiencies, training gaps, or underutilized features
- Refactor workflows or modify automation rules based on real-world usage
- Expand into adjacent modules like Service Level Management, Continuous Improvement, or Virtual Agent
- Evaluate platform governance and data hygiene practices to maintain long-term scalability
Optimization is a continuous process, turning ServiceNow from a service management tool into a strategic operations platform.
This phased approach balances speed with stability, allowing organizations to modernize IT operations while minimizing business disruption.
Stop trying to find the dots. Let us help you connect them! With GEM as your ServiceNow Partner, accelerate delivery, reduce complexity, and gain a competitive edge in today’s fast-changing market.
Integrating ServiceNow with Your IT Ecosystem
ServiceNow ITSM delivers the most value when it operates within a connected technology environment. Integrating it with surrounding systems creates a unified service management framework that supports faster decisions, improved visibility, and coordinated execution across teams.
Common Integrations: CMDB, Monitoring Tools, AIOps, HR, CRM
CMDB & Discovery Tools
Integration between ServiceNow and asset discovery tools (e.g., SCCM, Tanium, BMC Discovery) keeps the Configuration Management Database updated with accurate and current data. This provides a real-time view of configuration items (CIs) and their relationships, which supports impact analysis, compliance tracking, and automated incident triage.
Monitoring Tools
Tools such as SolarWinds, Nagios, Dynatrace, or Datadog can feed performance events and alerts into ServiceNow. When integrated, these monitoring platforms can automatically generate incidents in ServiceNow, enriching them with context and reducing mean time to detection and response.
AIOps Platforms
AIOps platforms like Moogsoft, BigPanda, or ServiceNow’s own ITOM Predictive AIOps can process high volumes of operational data to identify anomalies, correlate alerts, and recommend remediation steps. When connected with ServiceNow ITSM, they support proactive incident management and reduce alert fatigue.
HR Systems
Integrating ServiceNow with HR platforms (e.g., Workday, SAP SuccessFactors) helps streamline onboarding and offboarding workflows. Automated account provisioning, role-based access setup, and asset allocation are examples of cross-functional workflows supported by this integration.
CRM Systems
Linking ServiceNow with CRM tools (e.g., Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics) creates a bridge between customer-facing teams and IT operations. This allows for better tracking of customer-impacting issues, shared visibility into service histories, and coordinated resolution efforts.
Data Alignment and the Role of CSDM
At the center of these integrations is the Common Service Data Model (CSDM), which provides a standardized schema for mapping services to underlying infrastructure and business functions. CSDM acts as a reference architecture, ensuring that data from external systems is aligned with ServiceNow’s service definitions and relationship models.
- CSDM enables consistent service mapping across ITSM, ITOM, and ITBM modules
- It supports traceability from business services down to individual components or applications
- With CSDM in place, reporting, impact analysis, and root-cause investigations are based on a shared understanding of service structure
Managing Change Across Multiple Systems
When ServiceNow is integrated into a broader IT ecosystem, managing change becomes more complex but also more impactful. Key considerations include:
- Coordinated workflows that reflect dependencies across systems (e.g., database changes triggering application updates)
- Automated risk assessments based on CMDB relationships and change history
- Change notifications propagated to affected systems and stakeholders
- API-driven updates to synchronize status across project management, deployment, or monitoring platforms
A successful integration strategy turns ServiceNow into a central coordination layer, where actions in one system trigger data flows and updates across others, reducing silos and improving operational continuity.
Read more: Learn how ServiceNow integrations reduce change risk and keep complex systems in sync.
Optimizing ServiceNow ITSM for Long-Term Impact
Implementation is only the starting point. To realize sustained value from ServiceNow ITSM, organizations must treat it as an evolving platform, continually refined through automation, measurement, and alignment with changing business needs.
Automating Routine Tasks with Workflows and AI
Manual processes slow down service delivery and increase the risk of error. Automating high-frequency, low-complexity tasks helps IT teams focus on exception handling and strategic initiatives.
- Workflow automation handles ticket assignment, approval routing, escalation, and notifications
- AI-driven features like virtual agents can resolve common requests (e.g., password resets or access requests) without human intervention
- Machine learning models can categorize incidents, recommend solutions, or predict SLA breaches based on historical patterns
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can bridge gaps between ServiceNow and legacy systems that lack APIs
Using Analytics to Identify Improvement Areas
Analytics provides the foundation for continuous improvement. By analyzing performance data across ITSM modules, organizations can uncover trends, bottlenecks, and unmet demand.
- Dashboards track KPIs such as MTTR, SLA compliance, backlog volume, and request fulfillment time
- Trend analysis identifies recurring issues or areas with rising service demand
- Root-cause analytics help isolate systemic failures that impact multiple services
- Heatmaps and workload distribution data inform staffing and process design
Continuously Aligning ITSM with Business Priorities
ITSM must evolve alongside the business. Changes in business models, customer expectations, or digital investments often require corresponding shifts in service processes and platform capabilities.
- Regularly review service portfolios to retire low-value offerings and introduce new ones
- Adjust SLAs based on business expectations or operational capacity
- Expand into adjacent ServiceNow modules (e.g., ITOM, SPM, or HRSD) to support cross-functional workflows
- Conduct stakeholder reviews and feedback cycles to validate service relevance and usability
A long-term perspective on ServiceNow ITSM shifts the focus from technical deployment to operational transformation. Integration, automation, analytics, and alignment form the pillars of a sustainable, high-performing service management environment.
Read more: Explore the ITSM vs ITOM comparison to understand their roles in creating a resilient IT ecosystem.
How to Choose the Right ServiceNow Partner?
Selecting the right ServiceNow partner is a strategic decision that directly influences the quality, speed, and long-term value of your ITSM implementation.
Depth of ServiceNow Expertise
The first indicator of a qualified partner is the depth and relevance of their ServiceNow expertise. This includes both individual certifications and organizational specializations recognized by ServiceNow.
- Look for official designations such as Elite or Premier Partner status
- Evaluate certifications across key roles – architects, developers, implementation specialists
- Verify competencies across ITSM, ITOM, CSM, and other relevant modules
- Assess their familiarity with frameworks like CSDM, Agile, and DevOps in a ServiceNow context
Partners with broad and deep expertise are better equipped to handle complex configurations, anticipate technical dependencies, and design for scale.
Proven Track Record with Similar Implementations
Experience with organizations of similar size, complexity, and industry is a strong predictor of implementation success. A credible partner should be able to demonstrate outcomes, not just completed projects.
- Request case studies or references that align with your sector or use case
- Examine project scope, duration, and results delivered (e.g., SLA improvement, automation levels, adoption rates)
- Assess their ability to integrate ServiceNow with enterprise systems such as ERP, CRM, and monitoring tools
- Understand how they managed data migration, change control, and stakeholder engagement
Reputable partners can articulate not just what they did, but how they solved challenges comparable to your own.
Post-Deployment Support Capabilities
Sustaining value from ServiceNow requires ongoing support, optimization, and governance. Partners should offer structured post-deployment services that go beyond basic troubleshooting.
- Evaluate their managed services or support offerings, including SLAs and response times
- Understand their approach to performance monitoring, continuous improvement, and platform upgrades
- Confirm availability of advisory services for roadmap planning, release management, and capability expansion
- Ensure they have a model for proactive engagement, such as quarterly business reviews or health checks
A partner with a strong post-deployment model helps protect your investment and supports evolving business needs.
Ability to Align Tech Solutions with Business Outcomes
The most impactful ServiceNow implementations are those that connect technology to operational goals. A strong partner should begin with the business context, not just system requirements.
- Assess their approach to discovery and requirements gathering – do they map processes to outcomes?
- Understand how they measure success: Do KPIs focus on user experience, process efficiency, or cost savings?
- Review how they translate business needs into workflows, automation rules, and performance dashboards
- Determine if they can lead cross-functional conversations between IT, operations, and leadership teams
Partners that operate at both technical and strategic levels are better positioned to deliver lasting value.
GEM Corporation – Your Reliable ServiceNow Solution Partner

GEM Corporation is a global IT service company specializing in enterprise software, data services, and intelligent automation. Since 2014, we’ve partnered with forward-looking organizations in Japan, ANZ, Asia, the EU, and the US to deliver solutions that bridge business goals with digital execution. With over 400 IT professionals and a delivery portfolio spanning custom development, cloud, AI, and system integration, GEM combines technical depth with domain fluency.
Our ServiceNow practice is designed to move enterprises from scattered workflows to intelligent, connected operations. We tailor each implementation to your business context – focusing on near-term results, measurable ROI, and long-term scalability. From consulting and integration to managed services and platform optimization, GEM delivers full-cycle ServiceNow solutions that streamline processes and improve cross-functional collaboration. Using pre-built connectors, custom workflows, and AI capabilities, we simplify complex environments without disrupting core operations. Whether launching ITSM, ITOM, HRSD, or other solutions, GEM helps turn ServiceNow into a strategic growth platform.
Conclusion
ServiceNow ITSM plays a defining role in scaling IT operations by standardizing service delivery, integrating workflows, and enabling data-driven decision-making. Organizations that align ITSM practices with business priorities gain operational clarity, faster response times, and stronger cross-functional collaboration. With the right implementation strategy and long-term optimization, ServiceNow becomes a framework for enterprise agility. Contact GEM to explore how we can help you turn ServiceNow into a driver of measurable impact!
What are the key modules included in ServiceNow ITSM?
Core modules include Incident Management, Problem Management, Change Management, Request Management, Knowledge Management, and Configuration Management (CMDB). Each module is designed to streamline specific service functions while contributing to a unified service management framework.
How can companies measure the performance of their ITSM implementation?
Performance is typically measured using KPIs such as first-call resolution rate, mean time to resolution (MTTR), SLA compliance, ticket backlog, and user satisfaction scores. ServiceNow provides real-time dashboards and analytics to track these metrics and identify areas for improvement.
What does a phased implementation approach for ServiceNow ITSM look like?
A phased rollout often begins with core modules like incident and request management, followed by change and problem management. Subsequent phases may include CMDB integration, automation, and AI functionality. Starting with high-impact areas allows for faster value realization and manageable change adoption.
What should organizations consider when choosing a ServiceNow implementation partner?
Key criteria include platform expertise, domain knowledge, experience in similar industries, and a track record of successful deployments. The right partner should offer more than technical delivery, they should align ServiceNow capabilities with your operational goals and support long-term optimization.