Contents
- Overview of the IT Asset Management Market
- What is ServiceNow ITAM?
- Understanding the ITAM Process Flow
- What are the Types of IT Asset Management?
- Understanding Cloud Cost Management
- Benefits of ServiceNow ITAM
- What are the ISO standards for ITAM?
- Common ITAM Processes and Best Practices
- GEM Corporation – Your Trusted ServiceNow Solution Partner
- Conclusion
Managing IT assets at scale doesn’t stop at basic inventory tracking. ServiceNow ITAM gives organizations a structured way to identify assets, stay compliant, and stay prepared for audits. This article outlines how the ITAM process flow – Discovery, Compliance, and Audit – supports better control across hardware, software, and cloud environments. We’ll also cover key capabilities, process best practices, and how to align with standards like ISO 19770.
Let’s examine how each stage of the ServiceNow ITAM process contributes to a more accountable and data-driven asset management model.
Overview of the IT Asset Management Market
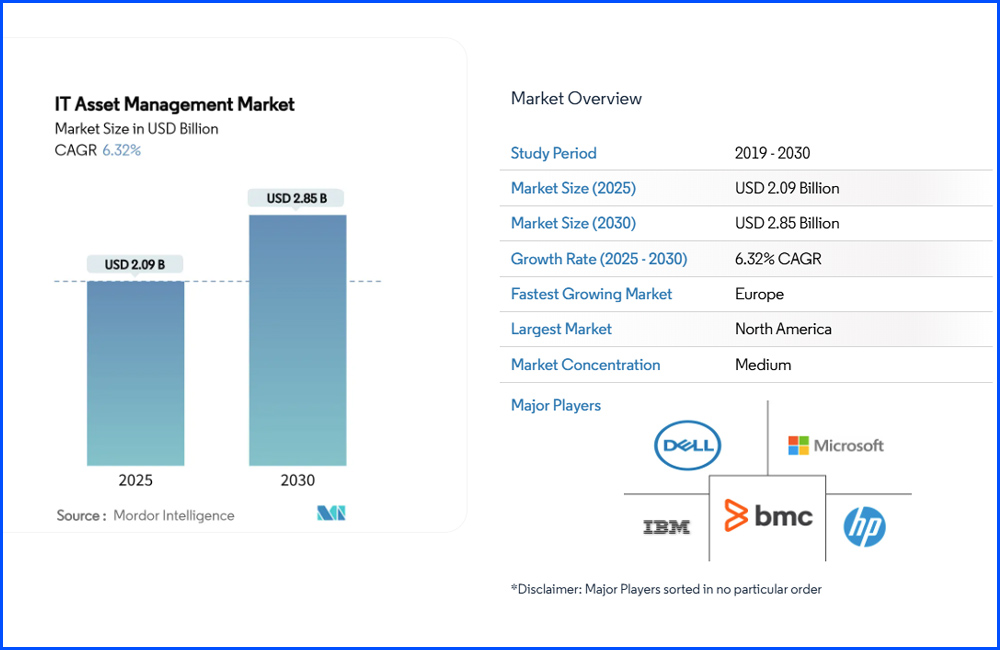
The IT asset management market is projected to grow from USD 2.09 billion in 2025 to USD 2.85 billion by 2030, reflecting a 6.32% CAGR. This momentum is driven by several shifts: hybrid-cloud adoption is accelerating, software audit risks are rising, and ESG compliance is gaining urgency. Organizations are now prioritizing unified platforms that offer full visibility into hardware, software, and cloud assets. AI-powered discovery tools and FinOps capabilities are no longer optional, they’re becoming standard as enterprises seek faster insights and better cost control.
What is ServiceNow ITAM?
ServiceNow IT Asset Management (ITAM) provides a structured approach to managing IT assets across their full lifecycle. It supports tracking from acquisition through usage to retirement, covering hardware, software, and cloud resources. The platform consolidates asset data into a single system, helping teams manage ownership, usage, and compliance across environments.
As part of the broader ServiceNow ecosystem, ITAM integrates with workflows like incident, change, and procurement. This connection helps break down silos between IT operations, procurement, and finance, offering clearer visibility and more coordinated decisions across departments.

Understanding the ITAM Process Flow
Understanding the ITAM process flow is central to building control, consistency, and accountability across IT environments. ServiceNow ITAM uses a structured model – Discovery, Compliance, and Audit – to help organizations manage assets with greater accuracy and readiness.
1. Discovery
This stage focuses on identifying all assets across on-premise, cloud, and hybrid environments. ServiceNow Discovery plays a key role by automatically scanning networks to detect devices, applications, and services. The data is then populated into the Configuration Management Database (CMDB), providing a current and reliable foundation for asset records. Discovery also closes visibility gaps, especially in areas where manual tracking leads to incomplete inventories or shadow IT.
2. Compliance
Once assets are identified, the next step is to determine if their usage aligns with licensing terms, entitlements, and internal policies. ServiceNow ITAM connects asset data with entitlement records to analyze software consumption and identify overuse or underuse. This supports both financial accountability and license optimization. The platform also tracks contract terms, renewal timelines, and usage thresholds, helping teams stay ahead of vendor audits and avoid compliance-related disruptions.
3. Audit
The final stage prepares the organization for both scheduled and unplanned audits. ServiceNow ITAM centralizes reporting and usage evidence, making it easier to demonstrate compliance with software agreements and regulatory requirements. Audit readiness also extends to risk monitoring, flagging inconsistencies, unsupported software, or aging hardware before they become operational or financial liabilities. With accurate records and traceable workflows, teams can respond to audit requests with less effort and more confidence.
What are the Types of IT Asset Management?
IT Asset Management (ITAM) spans multiple categories, each with distinct roles in managing the technology footprint of an organization.
Software Asset Management (SAM)
SAM focuses on tracking, optimizing, and governing the use of software assets, both on-premise and cloud-based. It brings structure to license management, spend visibility, and compliance tracking.
Key Capabilities:
Now Assist for SAM
This GenAI-driven assistant summarizes key software metrics, contract status, usage patterns, and compliance posture, offering contextual insights. It identifies unused licenses and surfaces risk areas without requiring manual audit cycles.
SaaS License Management
Tracks license entitlements and actual usage across SaaS platforms. It supports API-based integrations and scans financial records to uncover shadow IT and unauthorized subscriptions.
Explore more about SAAS platform: Snowflake vs Databricks
SAM Playbooks and Workspace
Guided workflows simplify complex licensing tasks like server entitlement setup or audit preparation. The workspace serves as a control center to monitor activities across the software lifecycle.
Software Spend Detection
Uses AI to match transactions to known software catalogs, flagging duplicate purchases and overlapping subscriptions. This helps reduce waste and consolidate tools.
Patch Tracking
Coordinates the rollout of software patches, aligning with internal security standards. It ensures version consistency and reduces exposure to known vulnerabilities.
Software Inventory and Application Control
Maintains detailed records on installed software, including version, location, and license metadata. Access control policies define who can use which applications, supporting governance and auditability.
Hardware Asset Management (HAM)
HAM handles the acquisition, tracking, and retirement of physical assets such as laptops, servers, and peripherals. It also includes consumables like toner or cables. Key Capabilities:
Hardware Asset Workspace
Offers a centralized interface for managing all hardware activities – inventory tracking, transfers, audits, and procurement. Mobile access supports field activities and location updates.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Metrics
Calculates the full lifecycle cost of each asset, from purchase to disposal. This includes maintenance, support, and downtime. These insights inform repair vs. replace decisions.
Hardware Normalization
Standardizes manufacturer and model data for easier cataloging and reporting. It improves procurement accuracy and simplifies inventory searches.
Lifecycle Automation
Automates key steps such as onboarding, change tracking, and disposal. This reduces manual processing and improves data accuracy.
Inventory Management
Monitors stock levels across warehouses and offices in real time. It tracks asset location, availability, and pending orders, supporting agile fulfillment.
Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)
EAM focuses on serialized and consumable assets across the broader organization, beyond IT. This includes tools, equipment, and facilities required for operational needs. Key Capabilities:
Self-Service and Catalog Access
Teams can browse available tools, submit requests, and trigger transfers or replenishment. This reduces reliance on manual coordination and improves turnaround times.
Performance Analytics
Dashboards provide a live view of asset health, usage patterns, and lifecycle stage. Alerts flag unusual activity or delays in maintenance tasks.
Asset Reservations
Enables scheduling and allocation of shared resources. Teams can pre-book equipment or facilities, improving planning and avoiding double bookings.
Operational Technology (OT) Management
Tracks industrial and field assets, including spare parts. It monitors asset condition and lifecycle timelines to avoid unexpected downtime and manage risk in critical environments.
Asset Management Executive Dashboard
The Asset Management Executive Dashboard consolidates insights across hardware, software, and cloud domains into a single decision-support interface. It is designed for IT and business leaders who need visibility into asset performance, financial exposure, and compliance status in one place. Key Functions:
Cross-Domain Visibility
The dashboard aggregates data across SAM, HAM, and EAM, offering a unified view of asset usage, aging trends, and lifecycle status.
Role-Based Metrics
Stakeholders can access tailored KPIs based on their function – procurement, finance, compliance, or operations. This supports targeted action without overloading users with irrelevant data.
Maturity and Roadmap Tracking
Organizations can define success criteria, monitor progress against strategic goals, and benchmark asset program maturity. This makes it easier to identify gaps and prioritize investments.
Compliance and Risk Monitoring
Visual indicators highlight areas of non-compliance or risk, such as overdue renewals, unlicensed software, or under-protected endpoints, enabling faster mitigation.
Contract and Renewal Management
Contract and Renewal Management spans across software, hardware, and enterprise asset categories. It provides a structured approach to managing supplier agreements, renewal timelines, and contract-related spend. Instead of relying on spreadsheets or fragmented tools, teams can manage the entire lifecycle in-platform. Key Functions:
Centralized Contract Repository
All contract data – terms, renewal details, associated assets, and financials – are stored in a single source. This simplifies access and reduces the risk of missed renewals.
Renewal Workflows
Automated workflows guide users through each stage: renewal request, asset validation, contract rate updates, approval routing, and purchase order management.
Expiration Alerts and Planning
The system flags contracts nearing expiration, allowing teams to engage vendors early, reassess asset value, and negotiate more favorable terms.
Linked Asset Intelligence
Each contract is tied to specific assets, making it easier to assess whether renewals align with current usage, performance, and business needs.
Understanding Cloud Cost Management
With the proliferation of SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS solutions, cloud cost transparency has become a board-level concern. ServiceNow’s Cloud Cost Management module provides a centralized view of cloud spend across departments and vendors, supporting both cost control and strategic planning. Key Functions:
Comprehensive Spend Tracking
Tracks cloud consumption across platforms and services, categorizing expenses by service, application, cost center, and department.
AI Services Spend Management
Monitors costs associated with AI workloads, including inference usage, training cycles, and third-party service consumption.
License Reuse (BYOL)
Supports license portability across hybrid environments. It estimates the impact of migration scenarios and updates license data dynamically as infrastructure changes.
Spending Optimization
Flags underused or idle resources, helping teams shut down waste and reallocate budgets. This includes identifying duplicate subscriptions or overlapping tools.
Procurement Consolidation
Brings shadow IT purchases and siloed procurement under a unified model. This supports bulk negotiation with vendors and improves internal approval workflows.
Budget Control and Reporting
Teams can set cloud spend thresholds, monitor budget adherence, and generate custom reports segmented by business unit or initiative.
Stop trying to find the dots. Let us help you connect them!
Benefits of ServiceNow ITAM
ServiceNow IT Asset Management introduces structure and visibility to how organizations manage software, hardware, and cloud resources.
Informed Planning
Access to real-time data on asset condition, usage, and lifecycle stage supports smarter planning. Teams can prioritize purchases based on actual need rather than assumptions.
Operational Scale
By automating asset intake, updates, and decommissioning, the platform reduces manual intervention. This creates room for IT teams to shift focus toward higher-impact work.
Spend Control
Asset usage patterns help identify underutilized hardware and software. This reduces unnecessary acquisitions and improves the return on existing investments.
Policy Alignment
License tracking and audit readiness are built into the system. This helps organizations align with software agreements and avoid penalties tied to non-compliance.
Asset Risk Awareness
By linking asset data to security, configuration, and support records, the platform helps surface gaps, such as outdated software or untracked endpoints, that could introduce risk.
Read more: Top Servicenow Modules
What are the ISO standards for ITAM?
The ISO/IEC 19770 family defines globally recognized practices for managing IT assets. These standards support consistency, transparency, and accountability across environments where asset governance is a priority.
ISO/IEC 19770-1
This section outlines a framework for ITAM processes. It sets expectations for governance, documentation, and operational alignment, helping organizations evaluate and improve their asset practices.
ISO/IEC 19770-2
Focuses on software identification. It defines a uniform structure for software ID tags, which helps systems recognize and categorize installed applications accurately.
ISO/IEC 19770-3
Covers software entitlements. It establishes how license terms, conditions, and consumption rules should be documented and interpreted.
ISO/IEC 19770-4
Introduces a model for metering resource usage. This is especially relevant in hybrid environments, where license consumption may span on-premise and cloud infrastructure.
ISO/IEC 19770-5
Serves as an introduction to the full standard. It defines terminology and provides a reference model for how the other parts work together.
These standards provide a baseline for organizations aiming to formalize and mature their IT asset management programs
Common ITAM Processes and Best Practices

Effective IT Asset Management (ITAM) depends on consistent practices that extend across departments, systems, and asset types. When structured correctly, these processes improve governance, reduce waste, and support stronger decision-making at scale.
1. Standardizing Asset Intake and Classification
Intake procedures often mark the first point of failure in asset tracking. Without standard formats and classification rules, assets enter the system with inconsistent attributes. Defining common intake workflows and applying structured categories, such as hardware type, software function, location, or cost center, ensures uniformity. This consistency improves downstream reporting, lifecycle planning, and integration with procurement and finance systems.
2. Running Regular Audits and Reconciliation Cycles
Audits validate asset records against physical or discovered data. Reconciliation compares actual usage and inventory with contract terms and procurement logs. These routines detect missing assets, unauthorized installations, and expired entitlements. Running them on a fixed cadence reduces blind spots and keeps the asset register aligned with operational reality.
3. Aligning Asset Lifecycle Actions to Business Timelines
Assets follow distinct lifecycles – procurement, deployment, maintenance, and retirement. Mapping these stages to business timelines ensures that resources stay relevant to current needs. For instance, extending refresh periods for non-critical devices or retiring unused software ahead of renewal dates can free up budget and reduce maintenance overhead. Lifecycle alignment also supports forecasting and capital planning.
4. Defining Role-Based Access and Ownership Models
Data quality improves when ownership is clear. Assigning responsibility to individuals or teams for specific asset categories adds accountability to updates, audits, and renewals. Role-based access limits who can modify records, reducing errors and maintaining control over sensitive information.
5. Maintaining a Reliable CMDB Through Clean Practices
The Configuration Management Database (CMDB) acts as the backbone for service delivery, incident response, and change tracking. To remain accurate, it requires reliable discovery tools, deduplication logic, and periodic validation. Clean records support better linkage between assets and related services, giving operations teams clearer pathways for resolution and impact analysis.
Implementing these practices within ServiceNow brings consistency and transparency to asset management. To get the most value from the platform, organizations should consider working with a certified ServiceNow partner. Partners bring deep platform expertise, proven implementation frameworks, and domain-specific insight that help reduce deployment risk and accelerate outcomes.
Read more: List of Problem Solving Strategies Names in ServiceNow
GEM Corporation – Your Trusted ServiceNow Solution Partner

GEM Corporation is a global technology consultancy with a track record of delivering complex digital transformation initiatives across industries. Since 2014, we’ve executed over 300 projects for clients in Japan, ANZ, Asia, the EU, and the US, driven by a team of 400+ engineers and consultants. Our approach combines deep domain knowledge with a technology-agnostic mindset, allowing us to align platforms like ServiceNow with real operational goals.
As a trusted ServiceNow partner, GEM provides full-cycle implementation, integration, and optimization services across ITSM, ITAM, HRSD, and CSM modules. Our delivery model is built around industry-aligned blueprints, enterprise-grade governance, and measurable outcomes. We help organizations build connected workflows, unify data across silos, and streamline service operations without disrupting existing systems. From roadmap to rollout, GEM brings platform expertise, architectural clarity, and execution discipline that clients can rely on at scale.
What does the Discovery → Compliance → Audit process flow look like in practice?
The process starts with automated discovery of assets across on-premise and cloud infrastructure. Once identified, assets are evaluated for compliance, covering licensing, lifecycle status, and usage. Finally, audit readiness is achieved through accurate reporting and policy alignment, reducing risk exposure and manual effort.
What types of IT asset management does ServiceNow support?
ServiceNow supports multiple ITAM types, including Hardware Asset Management (HAM), Software Asset Management (SAM), and Cloud Asset Management (CAM). Each module is designed to manage specific asset classes, but they work together through shared data and integrated workflows
How does ServiceNow ITAM contribute to cloud cost management?
ServiceNow enables organizations to track cloud resource usage, align consumption with licensing terms, and identify underutilized assets. These insights help finance and IT teams implement rightsizing strategies and improve budget forecasting, especially in multi-cloud environments.
What standards and best practices align with ServiceNow ITAM?
ServiceNow ITAM supports ISO/IEC 19770 standards, which define structured approaches for asset discovery, license reconciliation, and audit preparedness. Best practices include maintaining a normalized asset database, automating lifecycle updates, and integrating ITAM with ITSM and GRC systems for end-to-end control.
Conclusion
The ServiceNow ITAM process flow, spanning discovery, compliance, and audit, creates a structured approach to asset visibility and control. By connecting asset data with licensing terms, usage patterns, and policy frameworks, teams gain a reliable foundation for managing cost, risk, and operational integrity. Each stage reinforces the next, forming a continuous loop that supports strategic decision-making.
To explore how this can be tailored to your organization, Contact us for a consultation!