Contents
- What is ServiceNow?
- 12 ServiceNow Modules that will Transform Your Operational Performance
- IT Service Management (ITSM)
- IT Operations Management (ITOM)
- IT asset management (ITAM)
- Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)
- IT business management (ITBM)
- Human resource service delivery (HRSD)
- Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC)
- DevOps
- Security operations (SecOps)
- Change Management
- Field Service Management (FSM)
- Customer Service Management (CSM)
- How to Successfully Implement ServiceNow Modules?
- GEM Corporation’s ServiceNow Capabilities
- Wrap Up
- What is ServiceNow, and why are its modules increasingly critical to enterprise operations?
- Which ServiceNow modules are expected to drive the most impact in 2025?
- What’s the difference between ITSM, ITOM, and ITAM in practical terms?
- How can organizations decide which ServiceNow modules to implement first?
- What’s required for a successful ServiceNow module implementation?
ServiceNow’s subscription revenue reached $10.6 billion in the last year, reflecting a 26% compound annual growth rate from 2020 to 2024. That trajectory reflects how enterprises are scaling their use of ServiceNow modules to operationalize service delivery, asset oversight, and risk governance. As organizations face growing complexity across IT, HR, field operations, and compliance, these modules are playing a larger role in shaping connected workflows across these functions. This article outlines 12 ServiceNow modules positioned to define operational performance in 2025 and how enterprises are applying them across the business.
What is ServiceNow?
ServiceNow is an enterprise platform built to manage digital workflows across departments, systems, and teams.
It provides a unified environment for handling service requests, automating manual tasks, and structuring complex processes across IT, HR, operations, and customer-facing functions. Originally known for IT service management, ServiceNow has expanded into a broader suite of modules that support business-critical functions from asset tracking to risk management.
One of the platform’s primary advantages lies in its ability to centralize data and connect workflows across functions that typically operate in isolation. This allows organizations to respond faster, eliminate duplicate efforts, and maintain consistent records across the enterprise. ServiceNow’s architecture supports scalability, allowing organizations to standardize global operations while maintaining local flexibility.
The platform also supports automation across repetitive tasks, giving teams more time to focus on work that drives outcomes. With built-in capabilities for performance analytics, ServiceNow helps decision-makers monitor service delivery and identify areas for operational improvement.
As organizations look to replace fragmented systems with coordinated operations, ServiceNow is increasingly positioned as a strategic layer for managing enterprise-wide workflows through a single platform.
12 ServiceNow Modules that will Transform Your Operational Performance
ServiceNow’s platform structure supports a wide range of modules designed to address operational complexity across IT, infrastructure, asset oversight, and service delivery. These modules serve distinct functions, but together they create a unified framework for managing workflows, data consistency, and service quality.
IT Service Management (ITSM)
ITSM is designed to standardize service workflows within IT organizations. Teams use this module to register, route, and resolve incidents, manage service requests, and track change activities. It incorporates analytics features that give managers performance metrics tied to service efficiency and response time.
The ServiceNow module runs on the Common Service Data Model (CSDM), which links technical services to business functions. A virtual agent is also included to respond to routine queries across employee and customer channels.
Core functions:
- Incident and Problem Management
- Change and Release Management
- Knowledge Base and Service Catalog
- SLA Monitoring and Reporting
- Self-service Portals and Virtual Agent
- Workflow Designer and Automation Engine
Key applications:
- Streamlining ticket resolution across distributed teams
- Tracking service performance across business units
- Automating routine service requests with AI-powered workflows
IT Operations Management (ITOM)
The IT operations management market is valued at USD 36.3 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 64.9 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 12.30% (Mordor Intelligence).
ITOM focuses on infrastructure visibility and service continuity across systems, applications, and cloud environments. It brings together multiple data sources to detect service interruptions, identify root causes, and map dependencies between applications and infrastructure.
Teams apply this module to monitor system availability, track deployment status, and initiate automated responses to operational events. The predictive analytics engine supports early identification of performance degradation.
Core functions:
- Service Map Creation
- Event Monitoring and Correlation
- Discovery and Dependency Graphs
- Cloud Resource Oversight
- AIOps and Operational Intelligence
- Infrastructure Metrics
Key applications:
- Monitoring hybrid environments with multi-source telemetry
- Isolating root causes during service outages
- Coordinating remediation across infrastructure teams
Read more: Learn how ServiceNow ITOM boosts visibility, automation, and operational stability.
IT asset management (ITAM)
The IT Asset Management Market is projected to reach USD 2.09 billion by 2025 and grow at a CAGR of 6.32% to reach USD 2.85 billion by 2030 (Mordor Intelligence).
ITAM tracks the lifecycle of IT assets across hardware, software, and cloud environments. The module provides a consistent view of asset location, usage, and ownership from acquisition through retirement. It also supports audit readiness by maintaining records of licenses, warranties, and vendor contracts.
Asset data is linked to procurement and finance systems, giving leadership greater transparency into spending patterns and inventory accuracy.
Core functions:
- Hardware and Software Tracking
- Cloud Asset Inventory
- License and Contract Management
- Asset Cost Reporting
- Maintenance Records
- Vendor Relationship Data
Key applications:
- Controlling IT inventory across regional offices
- Monitoring software license utilization
- Managing contract renewals and warranty status
Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)
ServiceNow’s EAM module supports full lifecycle oversight of operational assets, including facilities, equipment, and infrastructure. It provides structured workflows for maintenance, inspection, and capital planning, and integrates asset data with financial, compliance, and operational systems.
Unlike ITAM, which focuses on digital and IT assets, EAM addresses physical assets across field operations, logistics, and production environments. Maintenance history, utilization trends, and depreciation schedules are all recorded within a single system of record, allowing operations teams to prioritize asset reliability and cost control.
This module is gaining traction in asset-heavy industries such as utilities, energy, transportation, and manufacturing, where unplanned downtime and fragmented records carry direct operational impact.
Core functions:
- Preventive Maintenance Scheduling
- Work Order Coordination
- Asset Condition Monitoring
- Inspection and Compliance Tracking
- Capital Planning
- Inventory and Spare Parts Oversight
Key applications:
- Structuring maintenance workflows across plant equipment
- Tracking asset performance across field locations
- Aligning financial planning with asset lifecycle data
IT business management (ITBM)
ITBM (now known as Strategic Portfolio Management – SPM) is structured to give decision-makers visibility into IT investments, project pipelines, and resource capacity. The module groups related initiatives under unified portfolios, with tracking across timelines, budgets, and business outcomes.
Project and demand data are centralized, supporting better alignment between strategic priorities and delivery teams. The module also includes tools for agile development, time tracking, and benefit realization, which support accountability across the full investment lifecycle. ITBM is increasingly used by technology leaders looking to prioritize projects based on business value, not just technical urgency.
Core Functions:
- Project and Portfolio Management
- Resource Allocation
- Agile Work Planning
- Budget and Cost Tracking
- Roadmap Visualization
- Innovation Intake and Evaluation
Key applications:
- Prioritizing IT programs based on executive goals
- Aligning delivery timelines with financial forecasts
- Tracking performance metrics across concurrent initiatives
Read more: Discover how ServiceNow SPM elevates strategic planning and portfolio execution
Human resource service delivery (HRSD)
HRSD provides a structured environment for managing HR requests, employee communications, and lifecycle events. It replaces fragmented email-based processes with service-oriented workflows that improve internal response time and record accuracy.
The module features a case management system for handling employee interactions, along with knowledge articles, onboarding task flows, and document storage. Employees interact through a centralized portal that routes requests to the appropriate HR function. HRSD is used by organizations aiming to standardize HR services across business units while improving transparency into case volumes, resolution times, and service quality.
Core functions:
- Employee Case Management
- Onboarding and Offboarding Coordination
- Knowledge Article Repository
- Document Generation and Storage
- Task Assignment and Workflow Routing
Key applications:
- Managing high-volume HR inquiries across regions
- Coordinating onboarding across multiple departments
- Tracking compliance actions tied to employee status changes
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC)
GRC on ServiceNow provides a structured framework for aligning oversight functions with business operations. It supports risk identification, policy tracking, control testing, and audit coordination within a single system. Teams use the module to maintain regulatory alignment and manage third-party risk exposure across departments.
Policy enforcement and issue response are integrated with real-time dashboards that surface control gaps and unresolved risks. The module also supports regulatory change tracking, so organizations can align quickly with new compliance requirements.
Core functions:
- Policy and Compliance Administration
- Risk Identification and Evaluation
- Control Testing and Monitoring
- Internal and External Audit Coordination
- Vendor Risk Reviews
- Regulatory Mapping
Key applications:
- Managing compliance across multiple jurisdictions
- Structuring audit trails for internal and external stakeholders
- Flagging operational risks tied to third-party vendors
DevOps
The DevOps module connects development, operations, and change management within a single environment. It supports continuous delivery pipelines while maintaining traceability across code changes, releases, and production deployments.
Integrations with external repositories and CI/CD tools bring real-time updates into ServiceNow, creating a consistent record of development activity. Teams use the module to track performance indicators, automate deployments, and manage change approvals without breaking compliance protocols.
Core functions:
- Agile Work Planning
- CI/CD Pipeline Integration
- Release Coordination
- Change Request Automation
- Environment Tracking
- Test and Quality Management
Key applications:
- Coordinating release timelines across global teams
- Maintaining audit trails across automated deployments
- Tracking velocity and throughput across development sprints
Read more: Learn how DevOps as a Service transforms software delivery with scalable, cloud-driven pipelines.
Security operations (SecOps)
SecOps brings incident response, vulnerability tracking, and threat intelligence into a unified system. It integrates with external detection tools to consolidate alerts, assign tasks, and track mitigation progress across cyber events.
Security teams apply the module to manage incident cases, prioritize vulnerabilities, and coordinate with IT for remediation actions. Dashboards provide visibility into open threats, resolution timeframes, and compliance tasks, supporting both tactical response and strategic oversight.
Core functions:
- Security Incident Case Management
- Vulnerability Intake and Prioritization
- Threat Intelligence Ingestion
- Task Assignment Across Teams
- Security Workflow Automation
- Compliance Evidence Collection
Key applications:
- Prioritizing vulnerabilities based on asset impact
- Coordinating incident response across security and IT teams
- Tracking remediation timelines for audit readiness
Change Management
Change Management in ServiceNow provides a structured process for planning, reviewing, and implementing changes across IT environments. It supports detailed tracking of change requests, with workflows that include risk assessments, stakeholder approvals, and implementation scheduling.
The module is tightly integrated with the Configuration Management Database (CMDB), providing context around affected services and dependencies. Teams use this context to evaluate potential business impacts and avoid service disruptions. The system enforces predefined approval paths and supports both standard and emergency change types. Activities are logged for audit purposes, supporting regulatory alignment and operational accountability.
Core functions:
- Change Request Registration
- Risk and Impact Analysis
- Approval Routing
- Change Calendar and Scheduling
- Emergency Change Tracking
- Change Advisory Board (CAB) Coordination
- Standard Change Templates
- Integration with CMDB
Key applications:
- Structuring reviews and approvals before infrastructure updates
- Avoiding unplanned outages during system changes
- Maintaining audit trails across change activities
Field Service Management (FSM)
FSM brings coordination to field operations by connecting work orders, scheduling, dispatch, and mobile task execution within a single system. It assigns technicians based on availability, location, and skill set, while syncing job data with central systems in real time.
The module is used across industries with distributed assets, such as utilities, telecom, and logistics, to align service performance with operational goals. Teams gain visibility into task status, technician location, and asset condition, reducing service delays and improving job accuracy. FSM also integrates with asset data and customer records, ensuring that field visits are based on complete and current information.
Core functions:
- Work Order Generation and Assignment
- Technician Scheduling and Dispatch
- Mobile Access to Task Details
- Location Tracking
- Parts and Inventory Coordination
- Real-Time Job Status Updates
- Integration with Asset and Customer Records
Key applications:
- Managing high volumes of field service visits
- Coordinating technician schedules with service-level targets
- Capturing field data to support asset performance records
Customer Service Management (CSM)
CSM provides a unified environment for managing customer interactions, resolving service issues, and coordinating case workflows. It consolidates product data, case history, and customer profiles in one record, supporting faster resolution and consistent service delivery.
The module includes tools for case segmentation, task assignment, and knowledge sharing. With built-in connections to field service and IT systems, CSM supports end-to-end service, from issue reporting to resolution, without manual handoffs. Use of CSM extends across industries where product complexity and service expectations require structured coordination between support, operations, and delivery teams.
Core functions:
- Case Management and Routing
- Customer Profile and Product Data Integration
- Knowledge Base Access
- Field Service Integration
- Task Tracking and SLA Monitoring
- Service Insights and Reporting
Key applications:
- Resolving customer issues without escalation across departments
- Coordinating support with field service teams
- Tracking service quality across customer segments
Stop trying to find the dots. Let us help you connect them! With GEM as your ServiceNow Partner, accelerate delivery, reduce complexity, and gain a competitive edge in today’s fast-changing market.
How to Successfully Implement ServiceNow Modules?
Deploying ServiceNow modules across an enterprise environment involves more than technical configuration. Success depends on how well the implementation aligns with operational objectives, integrates with existing systems, and scales across teams.
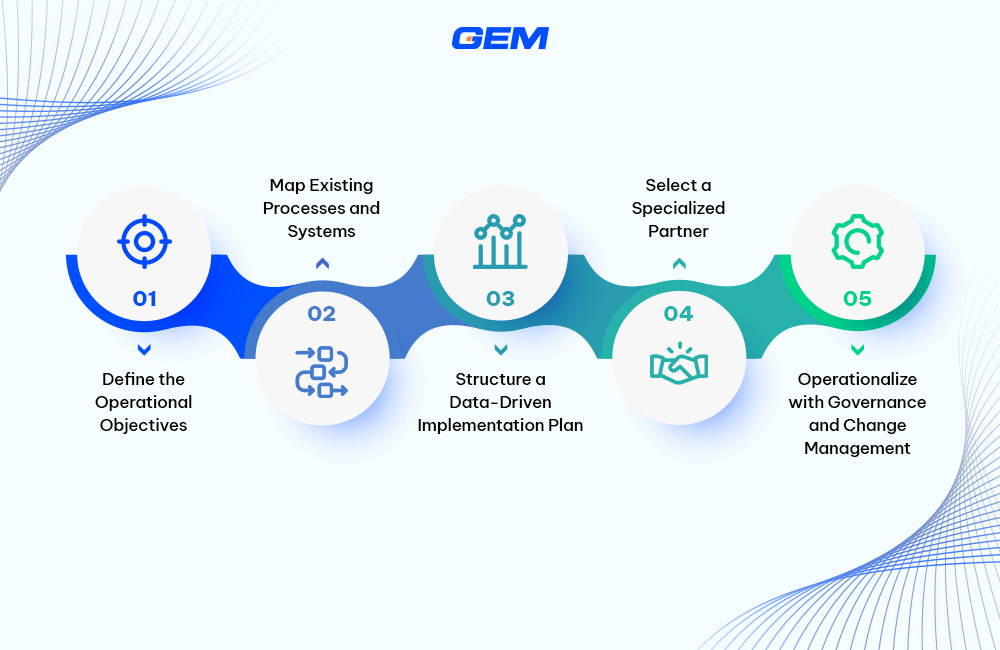
You can follow these 5 structured steps organizations follow to realize value from their ServiceNow investments:
- Define the Operational Objectives
Start by identifying the core business outcomes the platform should support, whether it’s faster incident resolution, improved asset visibility, or stronger compliance oversight. This clarity sets the foundation for selecting the right modules, structuring workflows, and establishing performance benchmarks.
- Map Existing Processes and Systems
A complete view of current workflows, tools, and data sources is necessary before configuration begins. This step reduces overlap, highlights integration points, and identifies process gaps that ServiceNow can address. Avoiding assumptions at this stage limits rework later in the cycle.
- Structure a Data-Driven Implementation Plan
Each ServiceNow module relies on accurate, structured data to function as intended. Organizations should assess data readiness early, especially where integrations with CMDB, ITSM, or asset inventories are involved. Implementation plans should also include testing cycles, migration checkpoints, and internal controls.
- Select a Specialized Partner
ServiceNow implementations require both technical depth and operational fluency. GEM works with enterprise teams to design and deploy platform configurations that reflect how the business actually runs. As a certified ServiceNow partner, GEM Corporation brings structured delivery models and domain-specific expertise across IT, field ops, and compliance functions. This reduces delays, limits scope creep, and accelerates time to value.
- Operationalize with Governance and Change Management
Post-deployment, teams must be equipped with clear usage protocols, training, and access governance. Ongoing platform governance, combined with performance tracking, ensures that modules continue to support business goals as operations evolve.
GEM Corporation’s ServiceNow Capabilities

GEM Corporation delivers end-to-end ServiceNow services across IT, employee, customer, and field operations. As a certified ServiceNow partner with over a decade of experience in IT services, GEM supports clients in implementing and scaling multiple modules, including ITSM, ITOM, ITAM, HRSD, CSM, and GRC.
Our teams combine platform expertise with industry knowledge to design solutions that reflect operational realities. Whether integrating with legacy systems, automating manual processes, or enabling AI-powered workflows, GEM structures each engagement around business outcomes. We assist from initial scoping through to post-launch optimization, addressing adoption, usability, and long-term scalability.
Backed by 400+ professionals and experience across banking, healthcare, manufacturing, and telecom sectors, GEM helps clients turn ServiceNow into a system of action that drives enterprise-wide efficiency.
Wrap Up
ServiceNow modules provide a structured approach to managing service delivery, asset oversight, risk operations, and customer interactions. When applied across functions, from ITSM and ITOM to HRSD, GRC, and CSM, these modules support consistency, transparency, and operational clarity. Success depends on clear goals, accurate data flows, and alignment with existing processes. Enterprises that approach implementation through a phased plan and bring in domain-specific partners, such as GEM, are better positioned to scale usage across teams. As organizations expand their use of ServiceNow modules, the priority will shift from deployment to measurable performance tied to business objectives.
To explore how ServiceNow modules can be structured around your operational goals, connect with our team for a tailored consultation.
Which ServiceNow modules are expected to drive the most impact in 2025?
While all 12 modules play a role in enterprise transformation, ITSM, ITOM, ITAM, HRSD, and CSM are seeing widespread adoption. Each brings distinct value: ITSM anchors service delivery, ITOM strengthens infrastructure visibility, ITAM manages asset lifecycles, HRSD supports employee services, and CSM connects service teams with customer operations. These modules are often deployed together to eliminate silos and improve end-to-end workflows.
What’s the difference between ITSM, ITOM, and ITAM in practical terms?
ITSM manages service processes such as incidents and changes; ITOM focuses on infrastructure health, discovery, and event management; ITAM governs the lifecycle of hardware, software, and cloud assets. These modules intersect at the CMDB but serve different operational goals - ITSM for service experience, ITOM for operational insight, and ITAM for cost and compliance control.
How can organizations decide which ServiceNow modules to implement first?
Prioritization depends on current maturity, pain points, and strategic objectives. ITSM is often the starting point, especially when service delivery is fragmented. From there, many organizations expand into ITOM or HRSD to automate infrastructure or employee services. A structured roadmap, supported by platform assessments, helps teams build incrementally while maximizing early wins.
What’s required for a successful ServiceNow module implementation?
Beyond licensing and configuration, success depends on three factors: process alignment, adoption planning, and integration strategy. Organizations need clear ownership, stakeholder buy-in, and a roadmap that connects platform features to measurable outcomes. Post-deployment, the focus shifts to optimization, refining workflows, enabling self-service, and expanding usage across business units.