Contents
- What is AI & Cloud Integration?
- How Cloud-Based AI Operates in Real Environments
- Strategic Components of AI & Cloud Integration
- Why Enterprises Are Re-architecting Around Cloud AI
- How AI & Cloud Integration is Reshaping Business Operations
- Barriers to Adoption: What Slows Down Cloud-AI Transformation
- The Road Ahead: AI-Driven Operating Models
- Why GEM Corporation Is the Right Partner for AI & Cloud Integration
- Conclusion
- What does AI and cloud integration mean in a business context?
- How are different industries applying cloud-based AI in practice?
- What are the key components of a cloud-AI operating stack?
- What are the main challenges businesses face when adopting AI in the cloud?
- Why is now the right time for organizations to prioritize AI and cloud integration?
Interest in cloud-based AI has grown steadily as companies seek to manage complexity across markets, systems, and teams. As more workloads shift to the cloud, business leaders are looking at how AI can support faster decision-making, stronger data visibility, and better coordination across operations. This article outlines the main components of AI and cloud integration, the gains it brings to workflows, and the considerations leaders face when scaling these capabilities across the organization.
What is AI & Cloud Integration?

The global cloud AI market is expected to reach $589.22 billion by 2032, up from $102.09 billion in 2025 (Fortune Business Insights).
AI and cloud integration, often referred to as Cloud AI, is the convergence of artificial intelligence and cloud computing. It gives businesses on-demand access to AI capabilities, such as machine learning, natural language processing, and predictive analytics, without having to build or maintain the underlying infrastructure. This setup allows companies to scale AI usage more affordably and focus on applying it to business problems, rather than spending months building models from scratch.
In business terms, Cloud AI is not just about hosting AI models on a remote server. It’s about embedding AI into the operational architecture – across infrastructure, data, and applications. This integration supports a shift from siloed experimentation to coordinated, cross-functional AI deployment. Companies can use cloud-native pipelines to ingest data, train models, and serve them through APIs directly into customer-facing systems or internal tools. Major providers such as Google Cloud, AWS, and Microsoft Azure are making these capabilities broadly accessible through prebuilt services and modular AI platforms.
How Cloud-Based AI Operates in Real Environments
Cloud-based AI functions through an end-to-end lifecycle that includes model training, inferencing, data integration, and API-level deployment. In practice, this means models are trained at scale using vast cloud infrastructure and then deployed to serve predictions in real time or near real time.
The process typically involves:
- Model training: AI models are trained using enterprise or third-party data on cloud platforms optimized for machine learning tasks.
- Inferencing: Once trained, models are deployed to respond to queries, deliver predictions, or classify data.
- Data linking: AI systems interact with various business data sources – CRM, ERP, customer interaction logs, to generate contextual outputs.
- API integration: Models are accessed through APIs, allowing them to be embedded into business applications and workflows without disrupting existing systems.
Deployment patterns vary by industry requirements. Companies in regulated sectors like finance or healthcare often use private or hybrid cloud environments to meet compliance and data residency standards, while others operate fully in the public cloud to gain flexibility and speed. We’ll explore these cases later in the article.
Strategic Components of AI & Cloud Integration
Building AI into the cloud requires a structured stack – connecting data, models, and applications in a way that supports scale, speed, and governance. Below are five core components that define how AI and cloud systems work together inside the enterprise.
- Unified Data Layer & Management Architecture
AI depends on context, and context comes from data. A unified data layer brings together structured and unstructured data across business systems, making it easier to train models and serve relevant outputs. Without this foundation, AI remains fragmented and hard to scale.
- AI Platforms & Model Pipelines (MLOps)
Businesses use cloud-based AI platforms to manage the full model lifecycle – training, tuning, deployment, and updates. MLOps frameworks help teams automate repetitive steps, version control their models, and track performance over time. This turns AI development from a one-off project into a repeatable process.
- API-first Integration Across Business Functions
APIs are the connectors between AI models and daily operations. They allow different teams – marketing, customer service, finance, to plug into AI tools without building custom infrastructure. With API-first design, businesses can scale AI use cases across departments with minimal friction.
- Inference & Orchestration Engines
Once models are deployed, inference engines serve predictions in real time or on schedule. Orchestration layers help coordinate these tasks based on business logic – when to trigger a model, what data to feed it, and where to route the output.
- Observability & Governance Layer
AI doesn’t stop at deployment. Businesses need clear visibility into model behavior, performance, and data usage. Cloud platforms offer built-in tools for monitoring, auditing, and access control. This layer helps maintain trust, internally and externally, as AI becomes more embedded in business decisions.
Why Enterprises Are Re-architecting Around Cloud AI
Cloud AI solutions are becoming a foundation for how companies run, scale, and respond to change. Business leaders are rethinking their tech stacks to take full advantage of what AI in the cloud can offer, both operationally and strategically.
Operational Leverage
- Cost-effectiveness: Cloud AI runs on a pay-as-you-go model. Teams get access to high-performance infrastructure without the capital investment of building it in-house.
- Scalability: AI workloads can grow or shrink based on actual demand. This flexibility helps avoid overprovisioning and supports experimentation without risk.
- Operational efficiency: AI automates repeatable tasks, manages data flows, and generates real-time insights that help teams move faster and with more confidence.
- Enhanced security: Major cloud vendors invest heavily in security. Combined with AI-driven threat detection, this setup can strengthen an organization’s defense posture.
Strategic Advantage
- Predictive analytics: AI helps leaders spot patterns early – market shifts, customer churn, inventory risks. This speeds up decision-making and sharpens forecasting.
- Personalization: Cloud AI systems track behavior across channels and adjust recommendations in real time. This creates more relevant experiences and drives long-term engagement.
- Cross-functional data visibility: Integrated AI systems allow different teams to work from the same data layer. This reduces silos and improves coordination across business units.
Risk & Resilience
- Security via AI-defined threat detection: AI tools can scan for anomalies and flag potential breaches faster than manual systems, adding a layer of proactive defense.
- Data quality improvement: AI can cleanse, standardize, and monitor data continuously. This supports compliance and improves downstream model accuracy.
- More agile response to change: With modular, cloud-based AI systems, companies can adapt faster, whether to market shifts, regulatory updates, or internal needs.
How AI & Cloud Integration is Reshaping Business Operations
AI adoption is moving fast across industries. According to Netguru, 78% of organizations globally now use AI in at least one business function. This marks a shift from isolated use cases toward enterprise-wide integration.
Below are six sectors where AI and cloud are increasingly shaping operations:
Retail
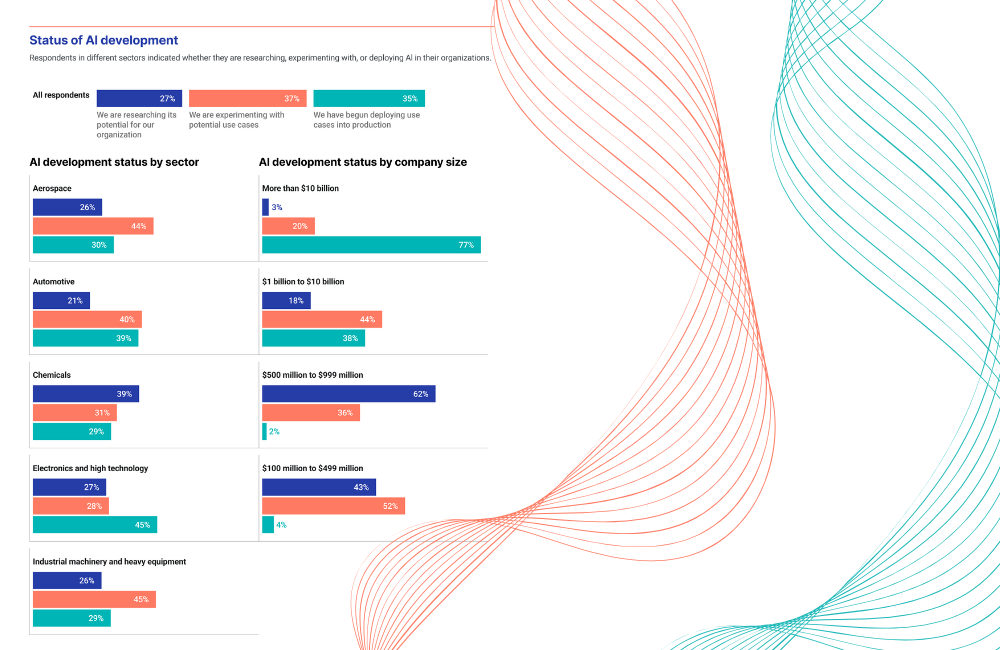
Source: https://www.coherentsolutions.com/insights/ai-adoption-trends-you-should-not-miss-2025
According to Deloitte’s 2025 US Retail Industry Outlook, Generative AI is proving to be valuable in commerce. Specifically, retailers experienced a 15% increase in conversion rates after utilizing chatbots during the Black Friday weekend. Retailers apply cloud AI to predict demand, optimize pricing, and personalize the customer journey. With access to real-time behavioral data across channels, businesses can tailor offers, adjust inventory, and improve conversion rates. Cloud integration also simplifies experimentation, enabling teams to test new AI models without operational delays.
Healthcare
AI models are being used to support clinical decisions, flag potential risks, and harmonize patient records across systems. Cloud-based platforms allow hospitals and research units to process large volumes of imaging data, lab results, and patient histories without local infrastructure. The AI healthcare market is projected to reach $36.96 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 36.83% (Precedence Research), driven largely by cloud-enabled diagnostic and support tools.
Finance
The BFSI sector leads AI adoption, accounting for 19.6% of global AI market share. Cloud-based AI helps financial institutions detect fraud, assess risk, and power algorithmic trading engines. Yet, despite high adoption, 97% of financial services organizations cite data silos as a barrier to scaling AI, highlighting the need for integrated cloud data platforms.
Manufacturing
AI is helping manufacturers reduce downtime and improve planning accuracy. Over 77% of manufacturers have implemented AI in some form, up from 70% in 2023 (2025 State of AI in Manufacturing Survey). Popular use cases include predictive maintenance, quality control analytics, and supply chain optimization. Cloud-based models make it easier to analyze sensor data and adapt quickly to demand changes.
Education
Schools and learning platforms are using AI to deliver adaptive learning experiences. Models assess student engagement, tailor content, and provide real-time feedback. Cloud AI enables remote delivery at scale, with data flowing across learning management systems and digital content providers.
Logistics
AI in logistics is improving route optimization, fleet management, and real-time tracking. With cloud-based tools, logistics providers can adjust delivery schedules dynamically, forecast disruptions, and better allocate capacity across networks.
Barriers to Adoption: What Slows Down Cloud-AI Transformation
While AI and cloud adoption have accelerated, several structural challenges continue to slow full-scale transformation.
Legacy Systems and Fragmented Data
Many enterprises still rely on legacy infrastructure that isn’t built to support large-scale AI workloads. Data remains scattered across silos, slowing model performance and limiting business impact. In financial services, 97% of firms cite data silos as a top barrier to enterprise-wide AI deployment. This reinforces the growing need for unified data fabrics and cloud-native platforms.
Migration Complexity and Change Management
Moving systems to the cloud, restructuring data flows, and updating governance models require coordination across IT, operations, and compliance teams. Change management becomes a challenge, especially when AI adoption disrupts existing roles or workflows.
Lack of Unified Data Strategy
AI models are only as good as the data they learn from. Without a clear strategy to harmonize and govern data across business units, models remain narrow in scope and hard to scale. Organizations that invest in shared architecture and cross-departmental collaboration tend to see faster progress.
Data Privacy Frameworks
Privacy regulations like HIPAA and GDPR introduce strict requirements for data use. This pushes companies to adopt privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) and rethink how AI models are trained and deployed, especially in healthcare, finance, and government sectors.
Aligning AI Outputs With Business Context
AI predictions need to fit into real decisions. Without context, such as customer segments, supply chain constraints, or risk thresholds, model outputs can’t drive action. This disconnect often leads to stalled adoption, as business teams struggle to interpret or trust AI recommendations.
The Road Ahead: AI-Driven Operating Models
Operating models are evolving as AI becomes more embedded across business functions. What was once limited to data science teams is now extending into customer operations, supply chains, and product development. Cloud-based AI platforms are accelerating this shift by offering the flexibility to test, deploy, and scale AI capabilities across departments, without the overhead of building everything in-house.
Several trends are emerging. First, AI agents are gaining traction across industries, with businesses adopting goal-oriented systems that automate decision flows. Second, multi-agent collaboration, where different AI systems interact to handle complex tasks, is beginning to influence how workflows are structured. Third, organizations are starting to move from isolated use cases to more unified, AI-first architectures that integrate with cloud-native infrastructure.
These shifts point toward a new era of operations where AI not only supports decision-making, but also actively shapes how businesses respond to change. For companies planning long-term, the path forward involves rethinking systems, data, and governance to support AI at scale. This raises a clear demand: to integrate AI and cloud as core enablers of business agility, not as separate technology layers.
Why GEM Corporation Is the Right Partner for AI & Cloud Integration
GEM Corporation supports businesses in deploying AI and cloud capabilities where they matter most – inside core operations. Since 2014, we’ve delivered tailored solutions for companies in finance, healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing across Japan, Asia-Pacific, and Europe. With 400+ engineers and consultants, our teams combine technical fluency with practical delivery.
Our AI services cover a wide range, from NLP chatbots and computer vision to generative models and predictive systems. These are built on cloud-native infrastructure, giving clients flexibility to scale across functions and regions. We work with modern DevOps pipelines and proven cloud platforms to shorten development cycles and simplify integration.
GEM is ISO 27001 and CMMI Level 3 certified, and a trusted partner of Databricks and ServiceNow. For businesses looking to operationalize AI without adding complexity, GEM offers the structure, tools, and domain knowledge to move from plan to production.
Conclusion
AI & cloud integration is reshaping how organizations operate – enabling faster decisions, connected workflows, and scalable infrastructure. As adoption grows, the focus is shifting from isolated pilots to coordinated, cross-functional systems. Success depends on aligning data, systems, and teams around a shared AI strategy. Companies that act now are in a stronger position to respond to change and capture new value. GEM Corporation works with business leaders to build practical AI-cloud solutions that fit real operational needs. To explore how our team can support your transformation, get in touch with GEM today!
How are different industries applying cloud-based AI in practice?
Industries are using AI in specific, outcome-driven ways. Healthcare organizations use it for clinical decision support and patient data harmonization. In retail, it powers demand forecasting and personalized experiences. Finance applies it in fraud detection and algorithmic trading, while manufacturers rely on AI for predictive maintenance and supply chain insights.
What are the key components of a cloud-AI operating stack?
A complete AI-cloud stack includes several layers: a unified data architecture, AI development platforms and pipelines (MLOps), API-based integration across business functions, inference and orchestration engines, and a governance layer for observability, compliance, and model monitoring.
What are the main challenges businesses face when adopting AI in the cloud?
Common barriers include legacy systems, fragmented data, and a lack of unified data strategies. Many organizations also face complexity in migration and change management, along with difficulties aligning AI outputs with real business context. Data privacy regulations further require strong architectural planning.
Why is now the right time for organizations to prioritize AI and cloud integration?
AI adoption is expanding across functions, with 78% of businesses already using it in some form. As cloud platforms mature and models become more accessible, integrating AI into core operations is becoming less about experimentation and more about long-term capability. Businesses that invest early are better positioned to scale, adapt, and compete.