Contents
Digital transformation is a critical strategy that organizations adopt to integrate digital technology into all areas of their business to change how they operate fundamentally.
A key enabler of this transformation is the Enterprise Service Bus (ESB). It is a central hub for integrating disparate systems, ensuring seamless communication, and enabling real-time data processing. This article explores the role it plays in digital transformation and its importance in integrating systems, maintaining data consistency, and providing flexibility and scalability for future growth.

Understanding ESB
Let’s first understand what the concept is, what it consists of, and how it works.
Definition
An enterprise service bus (ESB) is a software platform that facilitates the distribution of tasks among interconnected components within an application. It ensures a consistent method for transferring work to allow applications to link to the ESB and subscribe to messages based on straightforward structural guidelines and business policy rules.
Core components
Next, we discuss key components of the mentioned architecture.
Endpoints
Endpoints are considered the points to enter or exit the ESB, each of which has a unique identifier or addresser.
Various technologies can be used to implement endpoints, which range from message queues to FTP server and web service interfaces. In addition, endpoints can process different types of messages, such as binary data, XML, and JSON. As a result, the platform can integrate with a wide range of systems and applications.
Adapter
The adapter translates messages between different formats and protocols to ensure they are compatible with the recipient software applications. Additionally, it may offer functionalities such as logging messages, monitoring, authentication, and troubleshooting.
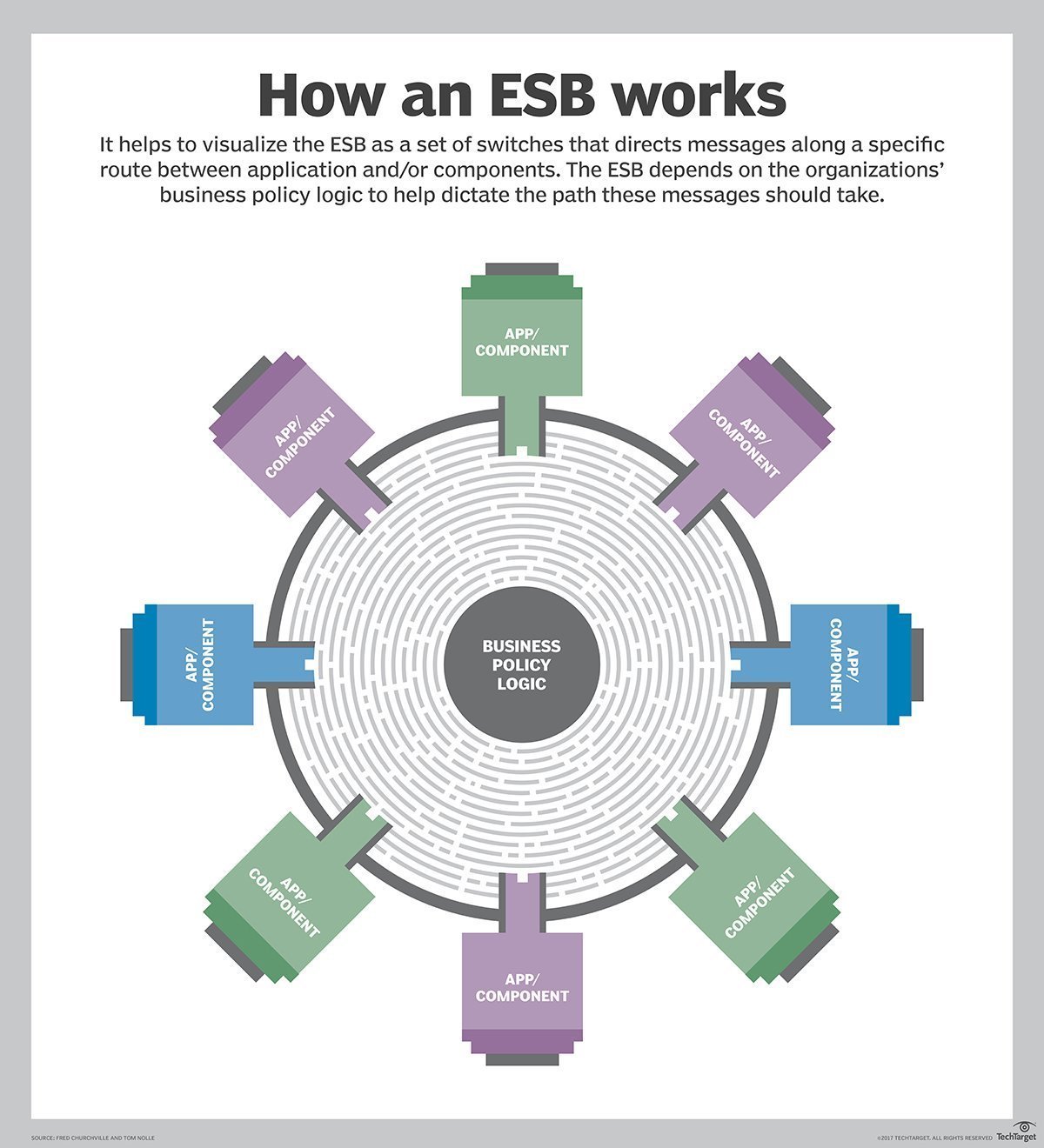
Bus
The bus is the central component that facilitates message exchange between endpoints. It routes messages based on predefined rules or policies, which can be defined in the ESB configuration to accommodate complex business processes. These policies consider factors such as message type, content, and destination. The bus supports various communication protocols, including HTTP, JMS, and FTP.

How does it work?
The bus receives messages at a designated endpoint. Afterward, it determines and transmits them to the destination endpoints by referring to business policy rules.
This structured approach ensures that messages are efficiently routed and processed based on predefined rules and policies.
For instance, when the bus receives an XML file from an application at endpoint A, it identifies that the file needs to be sent to endpoints B and C. Endpoint B requires the data in JSON format, while endpoint C needs it through an HTTP Put request. The adapter converts the XML file into JSON and the bus forwards it to endpoint B. Simultaneously, the bus sends the XML file via an HTTP request to endpoint C.
The importance of ESB in digital transformation
The role of this approach in digital transformation will become more pronounced in the future because their outstanding and advanced features support the scalability and flexibility required for modern digital ecosystems.
Enabling real-time data integration and process automation
As businesses strive to become more agile and responsive to market changes, ESBs will be essential in enabling real-time data integration and process automation. They will support the growing need for hybrid cloud environments, where businesses utilize a combination of on-premises, private cloud, and public cloud resources. They will facilitate seamless data flow and integration across these diverse environments, ensuring that businesses can leverage the best of each platform.
Fostering the personalization of user experience
Furthermore, as the demand for personalized customer experiences increases, ESBs will play a crucial role in integrating various customer touchpoints and data sources, providing a unified view of the customer and enabling personalized interactions at scale. The ability of ESBs to integrate and orchestrate services across different platforms will be key to achieving the holistic and connected digital ecosystems that future digital transformation initiatives will require.

Enhanced scalability
Digital transformation requires businesses to be agile and scalable. ESB provides the flexibility needed to adapt to changing business requirements by allowing companies to add or modify services with minimal disruption. This modular approach means that new services can be integrated without overhauling the entire system architecture.
Additionally, it enhances scalability by efficiently managing the increased load that comes with growth. It can handle a higher volume of transactions and interactions between services and ensure that performance remains optimal as the business scales.
This scalability is crucial for supporting long-term digital transformation initiatives because it allows them to grow and adapt without being constrained by their IT infrastructure.
Strengthened data consistency and management
By synchronizing data in real-time, ESB prevents discrepancies that could arise from having multiple data sources. This real-time synchronization is crucial for maintaining data integrity and reliability and facilitating strategic decision-making.
Moreover, its ability to manage data centrally simplifies the process of data governance, making it easier to enforce data standards and policies across the organization. This level of control over data management is instrumental in creating a unified and accurate view of business operations, which is essential for effective digital transformation.

Integration with new technologies
The integration of this method with advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain is paving the way for innovative solutions and business models. AI integration with ESB allows for intelligent data routing and processing, where AI algorithms can analyze data in transit and make real-time decisions, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes. For instance, AI can help prioritize and route customer service requests based on sentiment analysis of incoming messages.
In the realm of IoT, ESB is becoming crucial for managing the vast amounts of data generated by connected devices. They enable the aggregation, processing, and distribution of IoT data to relevant applications and services, facilitating real-time monitoring and control of IoT ecosystems.
Moreover, the integration of this platform with blockchain technology is emerging to enhance data security and transparency. By enabling secure and tamper-proof data exchanges between services, it can support the implementation of blockchain solutions in areas such as supply chain management and financial transactions.

Closing remark
As businesses continue to navigate the complexities of digital transformation, ESB empowers them to respond swiftly to market changes and deliver personalized customer experiences. Therefore, embracing it as a core component of their digital strategy will enable businesses to build agile, scalable, and connected digital ecosystems, positioning them for success in the evolving digital era.
Now it’s your turn to transform!
Our IT outsourcing team is ready to assist you in transforming your system and strategies with ESB. Let GEM know how we can contact you and kick off the journey right now!